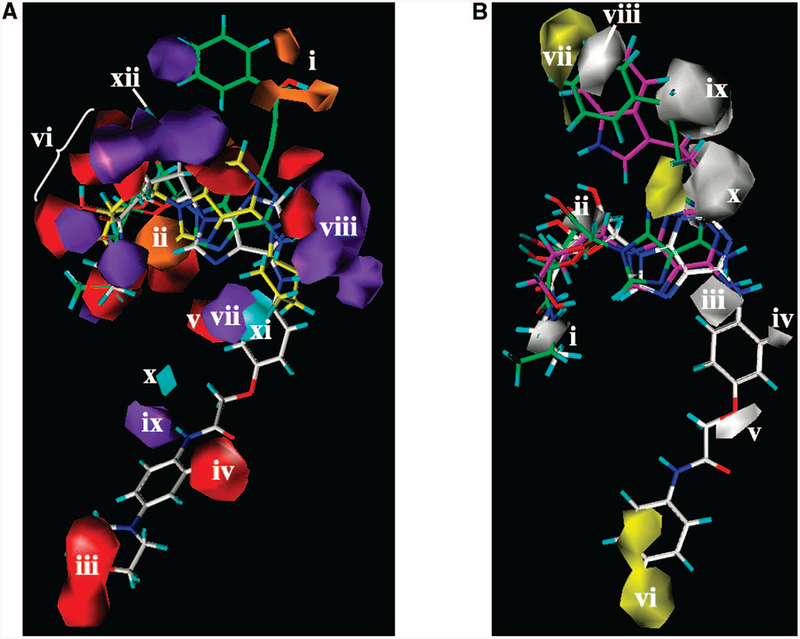
Figure 5.
(A) Contour maps of the CoMSIA H-bond donor and acceptor regions are shown around (S)-PHPNECA 2 (carbon atoms colored in green), CPA 3 (carbon atoms colored in yellow), and ligand 68 (carbon atoms colored in white): cyan plots, regions favored for the receptor H-bond acceptor groups; purple, regions disfavored for the receptor H-bond acceptor groups; orange, regions favored for the receptor H-bond donating groups; red, regions disfavored for the receptor H-bond donating groups. Region i appeared in proximity to the hydroxyl group of the 2-(3-hydroxy-3-phenyl)propyn1-yl moiety of (S)-PHPNECA 2 and (S)-PHPAdo 33. Region ii is located between the ribose oxygen atom and the 5’-OH group of the adenosine derivatives. Regions iii–v and vii–xi surround the N6 substituent. The group of regions vi and xii surround the 2’-and 3’-hydroxyl groups of the ribose moiety. (B) Contour maps of the CoMSIA hydrophobic regions (yellow, favored; white, disfavored) are shown around (S)-PHPNECA 2 (carbon atoms colored in green), MRS3997 4 (carbon atoms colored in magenta), and ligand 6 (carbon atoms colored in white) superimposed in their receptor-docked conformations. Polyhedral regions labeled with Roman numerals are discussed in the text. Region i corresponds to the 5’-position. Region ii is located in proximity to the 2’- and 3’-hydroxyl groups of the ribose moiety. Regions iii–visurround the N6 substituent, and regions vii–x appear around the 2 substituent.