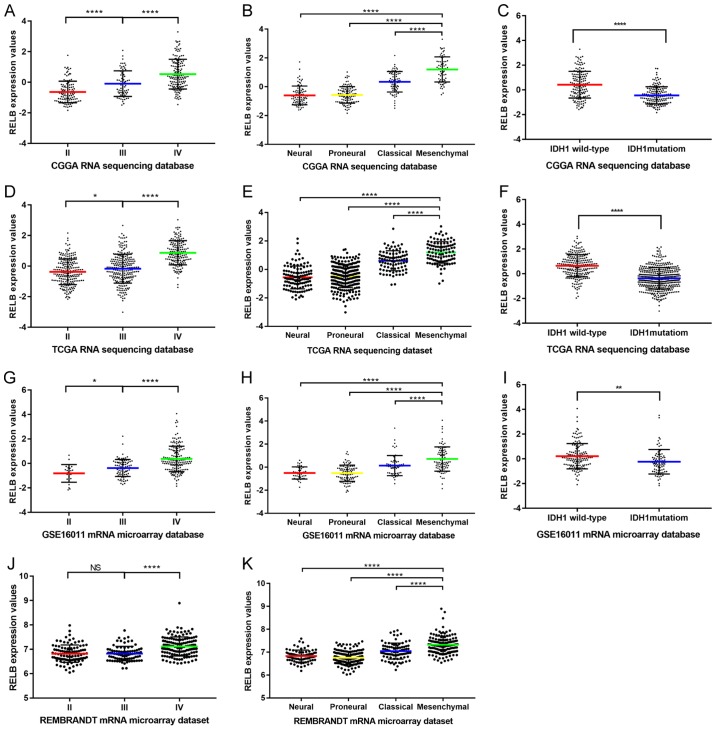
Figure 1.
RELB expression patterns in the CGGA database and other validation datasets. (A) The expression level of RELB in tissues from the CGGA database was positively correlated with tumor grade. (B) RELB expression was highest in mesenchymal subtype glioma samples from the CGGA database. (C) Patients with wild-type IDH1 had higher levels of RELB expression compared with those with mutant IDH1 in the CGGA database. (D) The expression level of RELB in tissues from TCGA database was positively correlated with tumor grade. (E) RELB expression was highest in mesenchymal subtype glioma samples from TCGA database. (F) Patients with wild-type IDH1 had higher levels of RELB expression compared with those with mutant IDH1 in TCGA database. (G) The expression level of RELB in tissues from the GSE16011 database was positively correlated with tumor grade. (H) RELB expression was highest in mesenchymal subtype glioma samples from the GSE16011 database. (I) Patients with wild-type IDH1 had higher levels of RELB expression compared with those with mutant IDH1 in the GSE16011 database. (J) The expression level of RELB from the REMBRANDT database was positively correlated with tumor grade. (K) RELB expression was highest in mesenchymal subtype glioma samples from the REMBRANDT database. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, as indicated. RELB, RELB proto-oncogene, NF-κβ subunit; CGGA, Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; REMBRANDT, Repository for Molecular Brain Neoplasia Data.