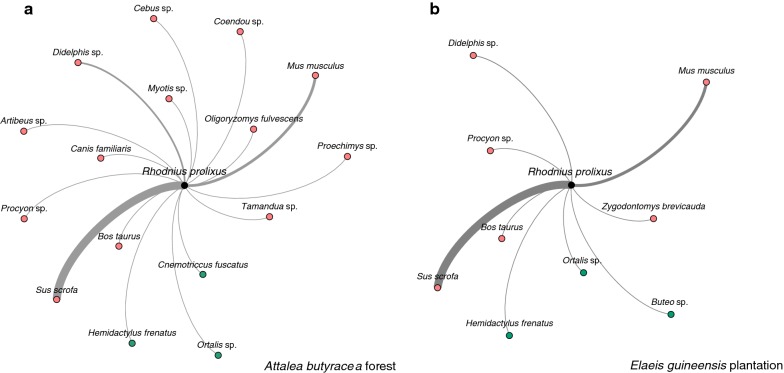
Fig. 1.
The interaction networks for Rhodnius prolixus blood meals the A. butyracea forest and the E. guineensis plantation. Nodes represent R. prolixus and vertebrate species. The vector node is colored in black, mammal nodes are pink colored, bird and reptile nodes are green colored. We considered unidirectional links, colored in gray, from every vertebrate species that provides a blood meal to the vector. Links vary in strength depending on the number of vector blood meals identified from each vertebrate species in a particular habitat. To determine link strength we normalized each blood meal species identified in R. prolixus. Therefore the link weight between the vector and the vertebrate species showing the highest number of blood meals is 1, which in both habitats is Sus scrofa, followed by Mus musculus and Didelphis sp