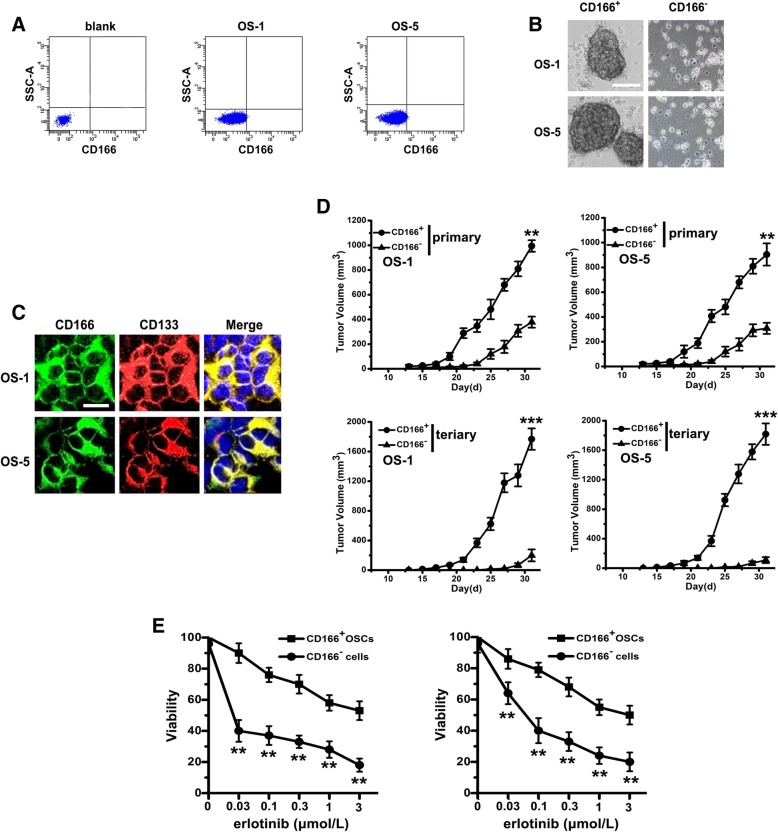
Fig. 1.
CD166+ cells from primary OS tissues display stem cell-like features and erlotinib resistant. a CD166+ cells were sorted from spheres by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. b Phase-contrast images of the ability of tumor spheres formation by seeding with CD166+ cells and CD166− cells in serum-free medium. Scale bar, 50 μm. c Immunofluorescent staining of CD166 (green) and CD133 (red) expression in CD166+ spheres (nuclei stained with DAPI). Scale bar, 10 μm. d With the presence of erlotinib, cell viability of CD166+ OSCs and CD166− cells were determined by MTT. Note: Columns, mean of three individual experiments; SD,** P < 0.01. e In vivo serial transplantation assay. A total of 10 4 CD166+ OSCs or CD166− cells from OS-1 or OS-5 in serum-free medium were injected s.c. into nude mice. Derived tumor xenografts were dissociated to single-cell suspension and then serially re-injected in mice (10 4 cells), generating secondary and then tertiary tumors. Tumor growth curves of primary and tertiary tumors are shown. Note: Columns, mean of three individual experiments; SD, *** P < 0.001; SD,** P < 0.01