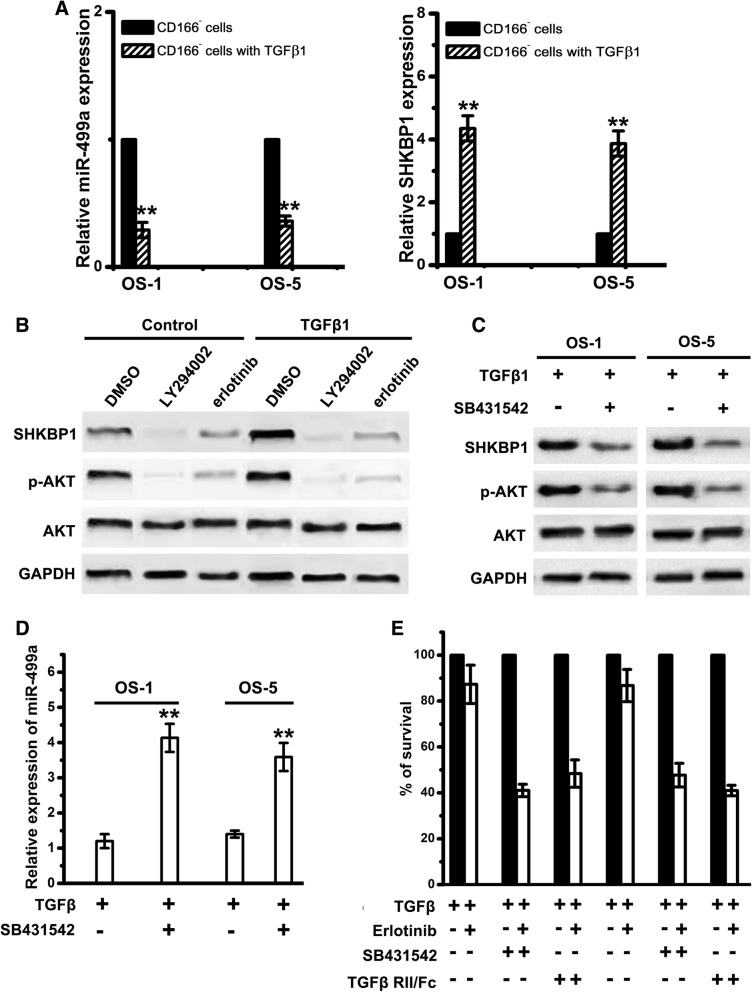
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of TGFβ signaling results in upregulation of miR-499a, decrease in SHKBP1 levels, and increased erlotinib sensitivity. a Relative expression of miR-499a and SHKBP1 in CD166− cells with or without TGFβ1 treatment were examined by qPCR. Note: Columns, mean of three individual experiments; SD,**, P < 0.01. b CD166+ OSCs treated with TGFβ1 or control vehicle for 21 day were exposed to LY294002 or erlotinib for 24 h. Immunoblot analysis was performed with antibodies against SHKBP1, AKT and GAPDH. c CD166+ OSCs treated with TGFβ1 or SB431542 were used for western-blot assays with antibodies against SHKBP1, AKT and GAPDH. d Relative expression of miR-499a in CD166+ OSCs with TGFβ1 or SB431542 were examined by qPCR. Note: Columns, mean of three individual experiments; SD,**, P < 0.01. e CD166+ OSCs were incubated with TGFβ (2 ng/mL) alone or in combination with either SB-431542 (10 m mol/L) or TGFβ -RII/Fc (20 ng/mL) for 7 days and then were treated with 1 m mol/L of erlotinib for an additional 72 h. Cell viability was assayed and values were set at 100% for untreated controls