Figure 1.
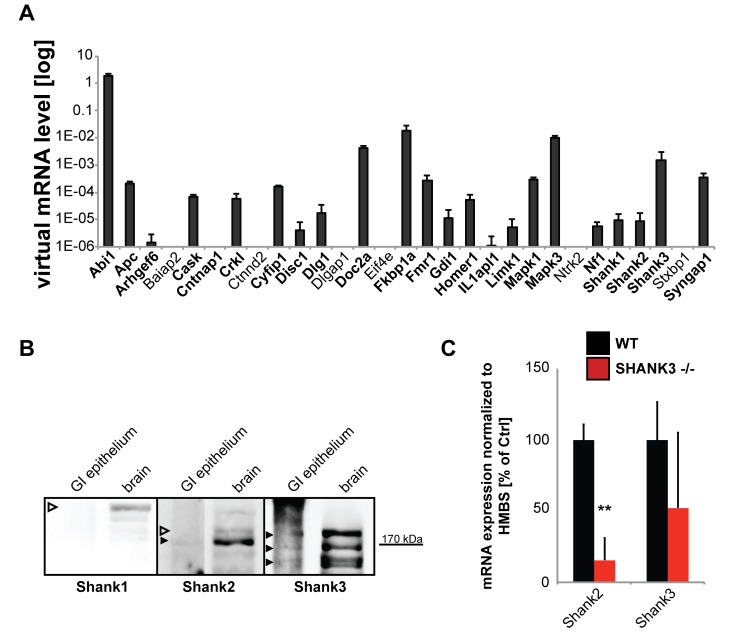
Expression of autism spectrum disorder (ASD)-associated postsynaptic density (PSD) proteins in gut epithelial cells. Several further ASD-associated PSD proteins are expressed in gut epithelial cells. (A) Screening of lysate from wild type mice (n = 5; used in technical triplicates) from isolated gut epithelium for the expression of “synaptic” ASD-associated genes using qRT-PCR. The genes were selected based on their occurrence at excitatory postsynapses and a reported association with ASD. On mRNA level, expression of all SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains (Shank) family members was detected, as well as the expression of several direct interacting proteins such as Abi1 (Abelson interactor 1), and Homer1 (Homer protein homolog 1). Furthermore, the expression of Apc (Adenomatous-polyposis-coli), Arhgef6 (Rac/Cdc42 Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor (GEF) 6, Alpha-PIX), Cask (Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Serine Protein Kinase), Cntnap1 (Contactin Associated Protein 1), Crkl (V-Crk Avian Sarcoma Virus CT10 Oncogene Homolog-Like), Cyfip1 (Cytoplasmic FMR1 Interacting Protein 1), Disc1 (Disrupted In Schizophrenia 1), Dlg1 (Discs, Large Homolog 1), Doc2a (Double C2-Like Domains, Alpha), Fkbp1a (FK506 Binding Protein 1A), Fmr1 (Fragile X Mental Retardation 1), Gdi1 (GDP Dissociation Inhibitor 1), Il1apl1, Limk1 (LIM Domain Kinase 1), Mapk1 and Mapk3 (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 1 and 3), Nf1 (Neurofibromin 1), and Syngap1 (Synaptic Ras GTPase Activating Protein 1) was detected. (B) Western Blot analysis for the expression of SHANK family members SHANK1, SHANK2, and SHANK3 using GI epithelium and brain tissue from wild-type mice. Only expression of SHANK2 and SHANK3 was detected on protein level in GI epithelium (full arrows). (C) Expression-analysis Shank2 and Shank3 in wildtype and Shank3αβ KO mice. Significantly lower expression of Shank2 was found in Shank3αβ KO mice (t-test, 3 technical replicates from 3 animals per group; Shank2 p = 0.0067 (n = 3); ** p < 0.01).