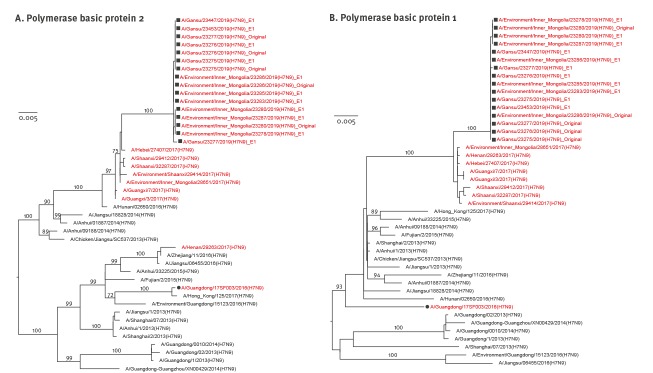
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analyses of the (A) polymerase basic protein 2 and (B) polymerase basic protein 1 gene segments of HPAI H7N9 viruses recovered from an infected patient and from environmental samples collected nearby, Inner Mongolia Autonomous region, China, April 2019
HPAI: highly pathogenic avian influenza; MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis; MUSCLE: MUltiple Sequence Comparison by Log- Expectation.
Multiple sequence alignments and maximum likelihood trees were conducted as for Figure 1 on the (A) polymerase basic protein 2 and (B) polymerase basic protein 1 genes. HPAI H7N9 viruses are highlighted in red. The investigated viruses and the candidate HPAI H7N9 vaccine strain are shown with a solid square and circle, respectively. Bootstrap values higher than 60 are shown. Horizontal distances are proportional to genetic distance, as shown by the scale bars.