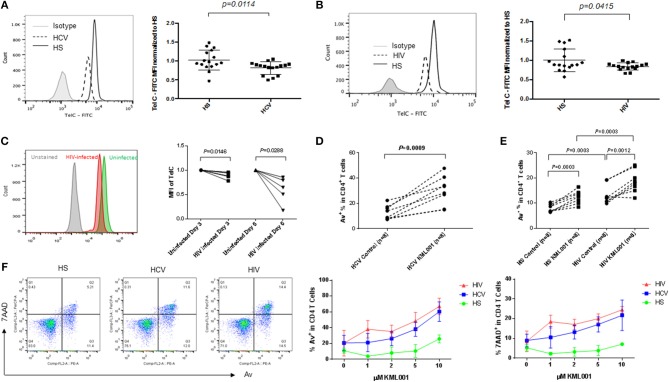
Figure 6.
CD4 T cells derived from HCV or HIV-infected individuals are more vulnerable to telomere loss-mediated apoptosis. (A,B) Telomere length, measured was by Flow-FISH, in CD4 T cells isolated from HCV- or HIV-infected individuals and HS. Representative overlaid histograms and summary data with mean ± SEM and p-values are shown. (C) Representative overlaid histogram and summary data of Flow-FISH analysis for telomere length in SupT1 cells infected with or without HIV-1 for 3 and 6 days. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of telomere length in HIV-infected cells are normalized by those in uninfected cells. (D) PBMCs derived from chronically HCV-infected individuals were treated with 5 μM KML001 or DPBS control for 24 h, followed by flow cytometry analysis of Av expression in CD4+ T cells. (E) PBMCs derived from latently HIV-infected individuals and HS were treated with 5 μM KML001 or DPBS control for 24 h, followed by flow cytometry analysis of Av expression in CD4+ T cells. Summary data with mean ± SEM (n = 8) and p-values are shown. (F) Dose-dependent induction of apoptotic death of CD4 T cells isolated from HCV- and HIV-infected individual and HS (n = 3 in each group) and exposed to varying concentrations of KML001 for 12 h. Representative dot plots of CD4+ T cells at 2 μM KML001 treatment and summary data of the dynamic changes of Av/7AAD levels in CD4+ T cells following varying concentrations of KML001 treatment are shown.