Figure 3.
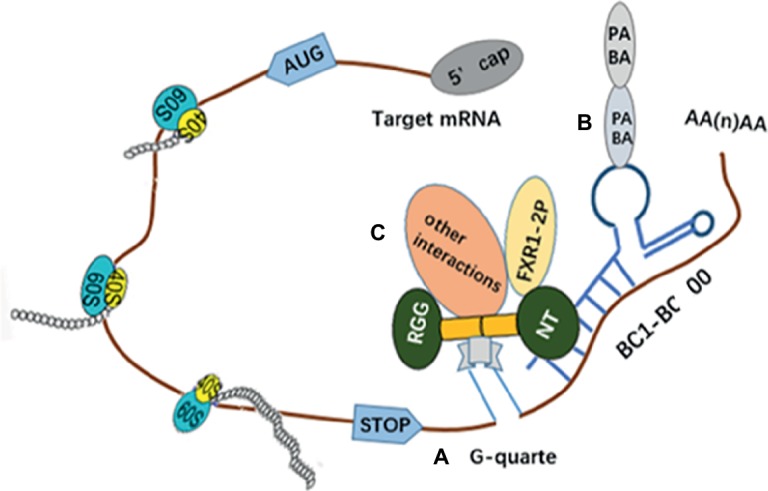
It is an illustration of how the BC2/200-FMRP complex recognizes and inhibits the translation of mRNAs. (A) The NT of FMRP can bind to the targeted mRNAs simultaneously via five regions of the longer stem loop of BC1 RNAs and G-quarter, and it would repress steadily the translation of the targeted mRNAs. (B) Poly(A)-binding protein (PABP) can connect with BC1 that actually act on the poly(A) tail of targeted mRNAs. (C) Other interactions also play a role in preventing the targeted mRNAs being.
