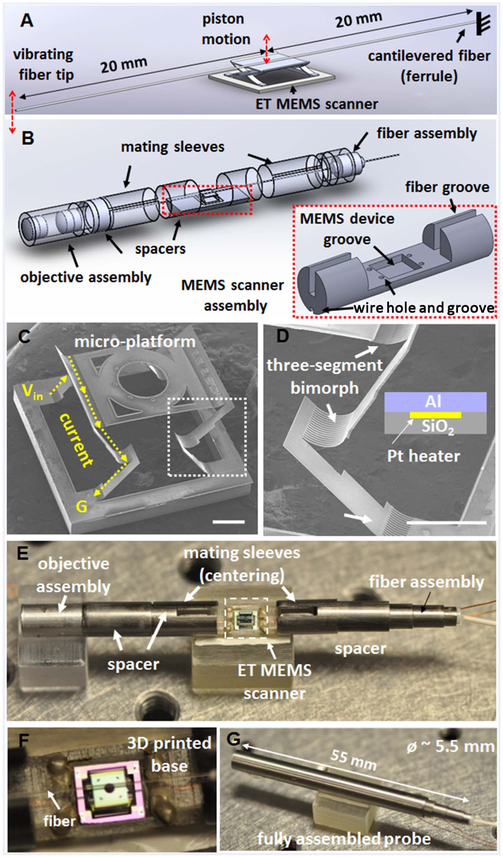
Fig. 1.
Schematics of (A) the fiber scanning mechanism and (B) the probe assembly, consisting of an ET MEMS actuator. (C), (D) SEM images of an integrated ET MEMS bimorph actuator; a micro-platform is supported and actuated by two pairs of three-segmented bimorph actuators with two connecting frames, which enable pure vertical motion with a large scanning amplitude. Scale bar: 500 μm. (D) Enlarged view of a three-segmented bimorph actuator [white boxed area in (C)]. ET bimorph actuator is composed of an Al, SiO2, and Pt layer. The Pt layer was sandwiched between the other two layers as a heating layer. Scale bar: 500 μm. (E) Photograph of the probe assembly; a 40 mm long fiber cantilever was mounted on top of the micro-platform of the ET MEMS scanner. (F) Magnified view showing the fiber was aligned with the center line of the ET MEMS scanner along the probe longitudinal axis. (G) Photograph of a fully integrated probe. Objective lenses and the fiber scanner were assembled with holders placed inside a hypodermic tube of a ~5.5 mm outer diameter and a 55 mm overall rigid length.