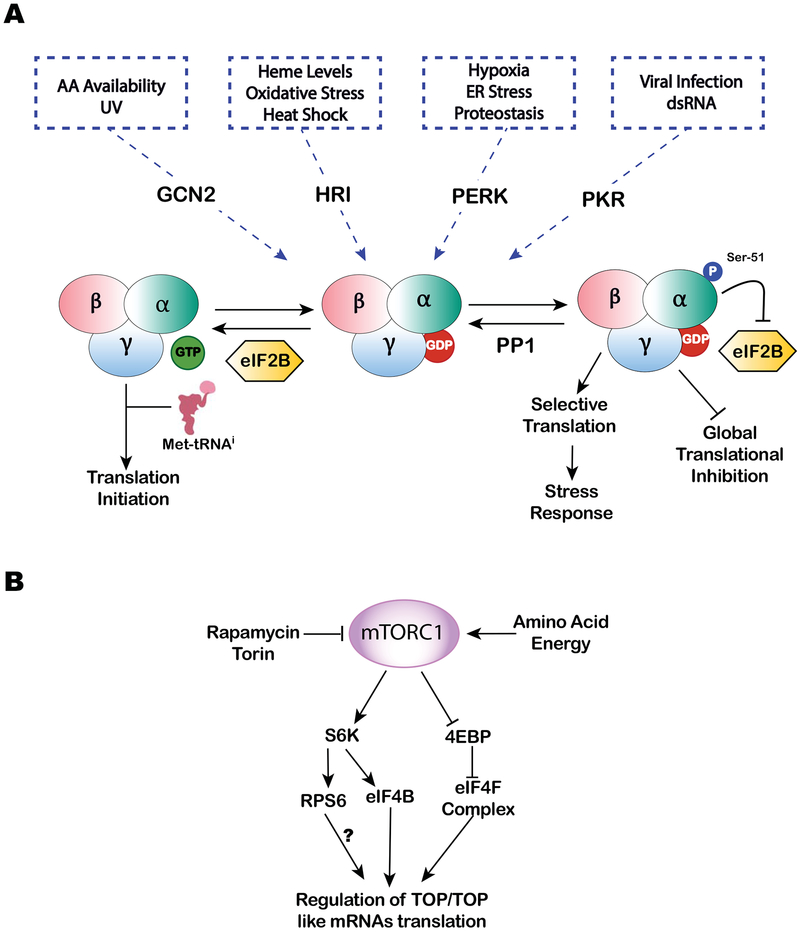
Figure 1.
A. The translation initiation ternary complex (TC) consisting of eIF2-GTP-Met-tRNAi is a part of 43S pre-initiation complex (PIC) required for cap-dependent translation initiation. Decoding of AUG ‘start’ codon at P-site leads to GTP hydrolysis and releases of eIF2-GDP. Phosphorylation of eIF2 at Ser-51 of the α-subunit by stress induced kinases GCN2 (UV and amino acid starvation), HRI (heme deficiency, oxidative stress and heat shock), PERK (hypoxia, ER stress and proteostasis) and PKR (viral infection and dsRNA) prevents GDP to GTP exchange by nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B, the step required to regenerate the TC. This stress-mediated eIF2α phosphorylation results in global cap-dependent translational inhibition, stimulates stress granule (SG) assembly and promotes selective translation of stress-responsive mRNAs. B. mTORC1 is a positive regulator of cap-dependent translation. Increased activity of mTORC1 results in the phosphorylation of translational repressor eIF4E-binding proteins (4E-BPs) and ribosomal S6 kinases (S6K½). These phosphorylation events are proposed to regulate translation of TOP/TOP like mRNAs. Treatment with mTOR inhibitors (e.g., rapamycin or Torin) or starvation conditions decreases the activity of mTORC1, thus inhibiting global translation and promoting stress responses.