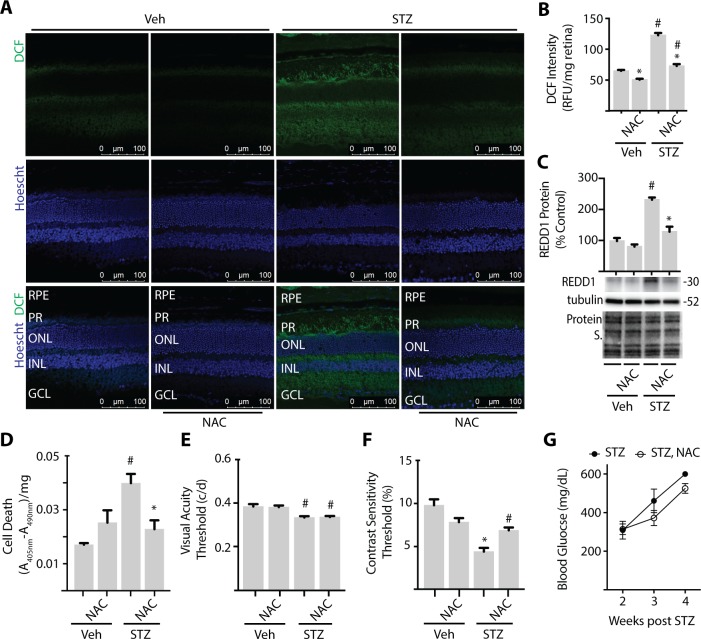
Figure 1.
NAC supplementation prevents retinal cell death and improves contrast sensitivity in diabetic mice. C57BL/6N mice were administered STZ or vehicle (Veh) for 5 consecutive days. Some mice received approximately 2 g/kg NAC via drinking water. Analysis was performed after 4 weeks of diabetes with or without NAC supplementation. (A) Whole-eye sagittal cross sections were exposed to 10 μmol/L DCF. (B) DCF fluorescence was quantified in retinal lysates. (C) REDD1 and α-tubulin expression were evaluated in retinal lysates by Western blotting. Gel loading was assessed via protein stain. Protein molecular mass (kDa) is indicated at right of blots. (D) Relative cell death was assessed by ELISA for cytoplasmic nucleosomes. Visual function was assessed by virtual optometry. Visual acuity (E) and contrast sensitivity (F) thresholds were obtained on consecutive days. The contrast sensitivity threshold is expressed as a reciprocal value. (G) Blood glucose was evaluated 2 to 4 weeks after mice were administered STZ. Results are from three independent experiments. Within each experiment three to four independent samples were analyzed. Values are means + SEM. Statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) are denoted by * for Veh versus NAC and # for Veh versus STZ. c/d, cycles/degree; RFU, relative fluorescent units; A, absorbance; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; PR, photoreceptor; ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer.