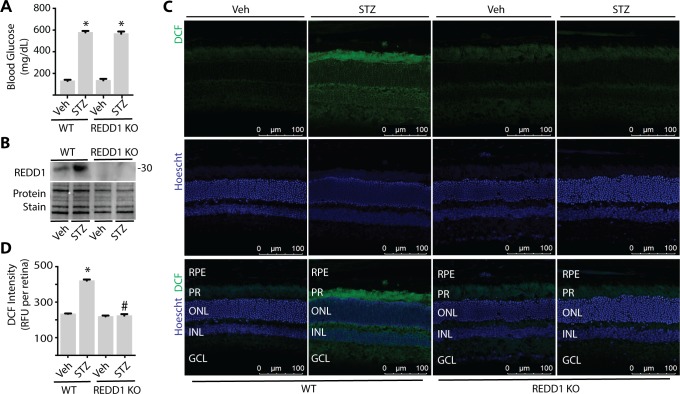
Figure 2.
REDD1 deletion is sufficient to prevent diabetes-induced ROS in retina. Diabetes was induced in wild-type (WT) and REDD1 KO B6;129 mice by administration of STZ. All analyses were performed 4 weeks after mice were administered STZ or Veh. (A) Postprandial blood glucose concentrations were evaluated. (B) REDD1 protein expression in retinal lysates was assessed by Western blotting. Protein loading was evaluated by reversible protein stain. Blot shown is representative of three independent experiments. Protein molecular mass (kDa) is indicated at right of blot. (C) Whole eyes were isolated, cryosectioned into sagittally oriented longitudinal cross sections, stained with 1.6 μM Hoechst, exposed to 10 μM DCF, and imaged by confocal laser microscopy. (D) ROS was quantified in supernatants from whole retinal lysates. Results are for three independent experiments. Within each experiment, three to four independent samples were analyzed. Values are means + SEM. *P < 0.05 versus Veh; #P < 0.05 versus WT.