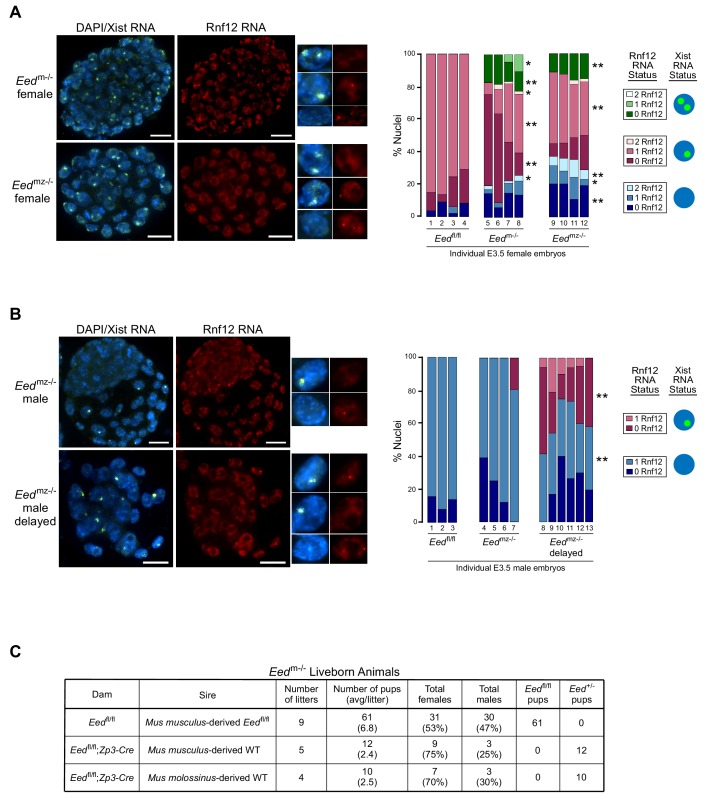
Figure 5. RNA FISH analysis of X-inactivation in Eedm-/- and Eedmz-/- blastocysts.
(A,B) RNA FISH detection of Xist RNA (green) and Rnf12 RNA (red) in representative Eedm-/- and Eedmz-/- female (A) and Eedmz-/- male (B) blastocysts. Nuclei are stained blue with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 µm. Individual nuclei of representative categories of stain are shown to the right of each embryo. Eedfl/fl female data from Figure 3D shown for comparison. Mutant female embryos ranged in size from 46 to 80 nuclei. Fully developed mutant male embryos ranged in size from 53 to 110 nuclei. Delayed mutant male embryos ranged in size from 30 to 40 nuclei. Bar plot shows percentage of nuclei in each embryo with Xist RNA coats and/or Rnf12 RNA expression. Each bar represents an individual embryo and embryo numbers under the bars correspond to the same female embryos plotted in Figure 4A. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01, Two-tailed Student’s T-test, between Eedm-/- and Eedfl/fl, or Eedmz-/- and Eedfl/fl. (C) Data showing the number of Eedm-/- embryos which can live to term compared to Eedfl/fl embryos. WT, wild-type. Table shows Eedm-/- litters sired by Mus musculus-derived male or Mus molossinus-derived male. Male Eedm-/- offspring are underrepresented compared to females, p=0.02, Two-tailed Student’s T-test.