Figure 1.
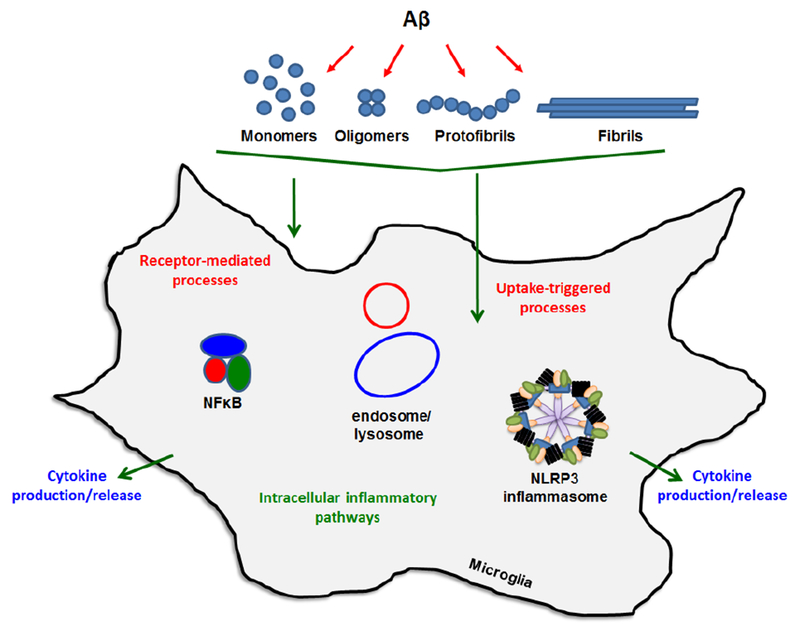
Mechanisms of Aβ-mediated neuroinflammation. Interactions between microglia and various conformational forms of Aβ involve stimulation of cell-surface receptors and internalization by non-receptor mechanisms. Either interaction can provoke pro-inflammatory cytokine release through multiple intracellular pathways. Two key processes involve NFκB-mediated transcription/translation of cytokines such as TNFα and pro-IL-1β followed by NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated cleavage of pro-IL-1β to mature IL-1β. Internalized Aβ can trigger inflammasome activity and this may occur via endosomal or lysosomal factors.
