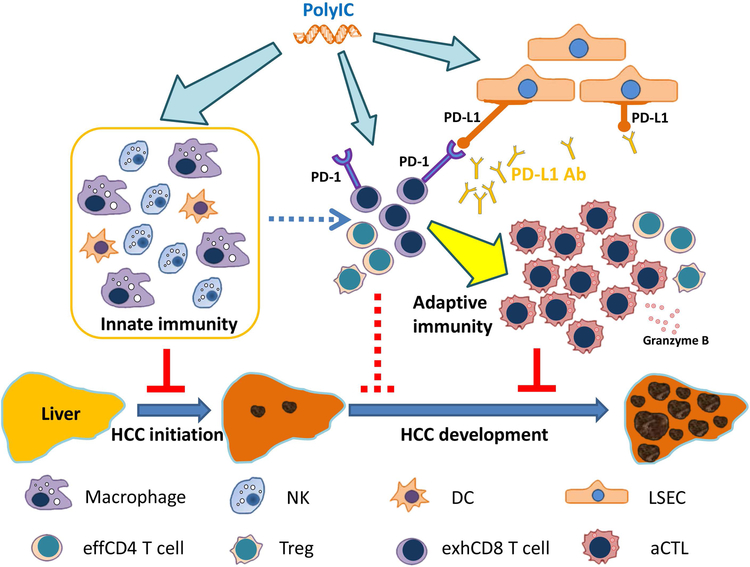
Figure 7. A model for the tumor-suppressing effects of polyIC and/or PD-L1 blockade.
Injection of polyIC suppresses tumor initiation by activation of multiple innate immune cell functions, and its induction of PD-L1 expression in LSECs sensitizes liver response to anti-PD-L1 blockade. Thus, a combined treatment of polyIC and PD-L1 Ab may be an effective combination immunotherapy for liver cancer.
NK: Natural killer cell; DC: dendritic cell; LSEC: liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; effCD4 cell: effective CD4 T cell; Treg: regulatory T cell; exhCD8 T cell: exhausted CD8 T cell; aCTL: activated cytotoxic T cell.