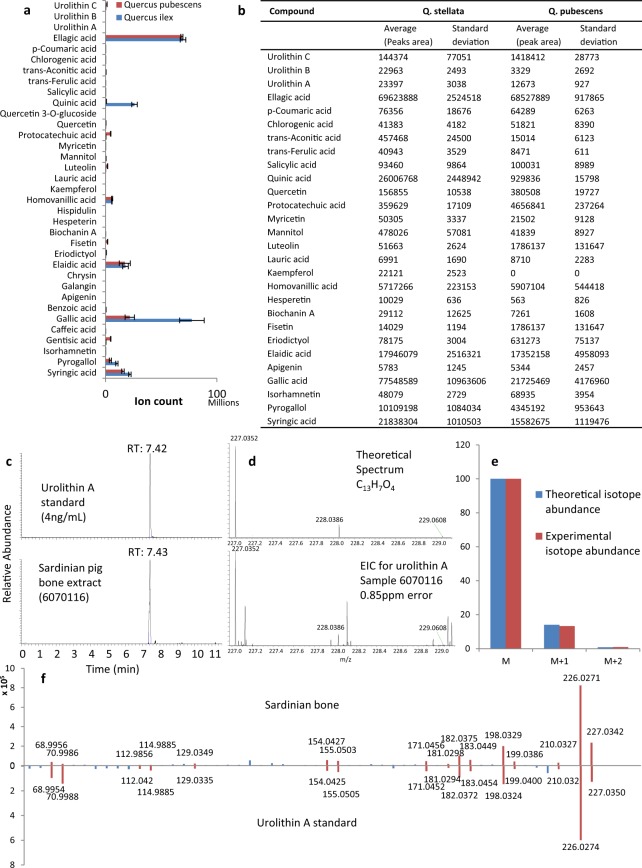
Figure 1.
Polyphenols identified in the acorn supplement and measurements for the identification of urolithin A in pig bone extracts. (a) Bar graph showing magnitude of the ion count for individual polyphenols identified in the acorn extracts (error bars St. dev. n = 9/group). (b) Average peak areas for plant secondary metabolites identified from acorn extracts (St. dev. n = 9/compound). (c) Chromatographic retention time for Urolithin A in the authentic standard and Sardinian bone 6070116 is 7.42 and 7.43 mins respectively, a difference of 0.6 seconds. (d) The accurate m/z measurement of Urolithin A in the authentic standard and Sardinian bone provided a difference of 0.85 ppm. (e) Comparison of the relative abundance of the M, M + 1 and M + 2 isotopes for Urolithin A in the authentic standard compared to Sardinian bone showed a 99% similarity. (f) Comparison of the product ion spectra from the collision induced dissociation (CID) of urolithin A (precursor m/z 227.03) in the Sardinian extract (top) and product ion spectra from the analysis of the urolithin A standard (bottom).