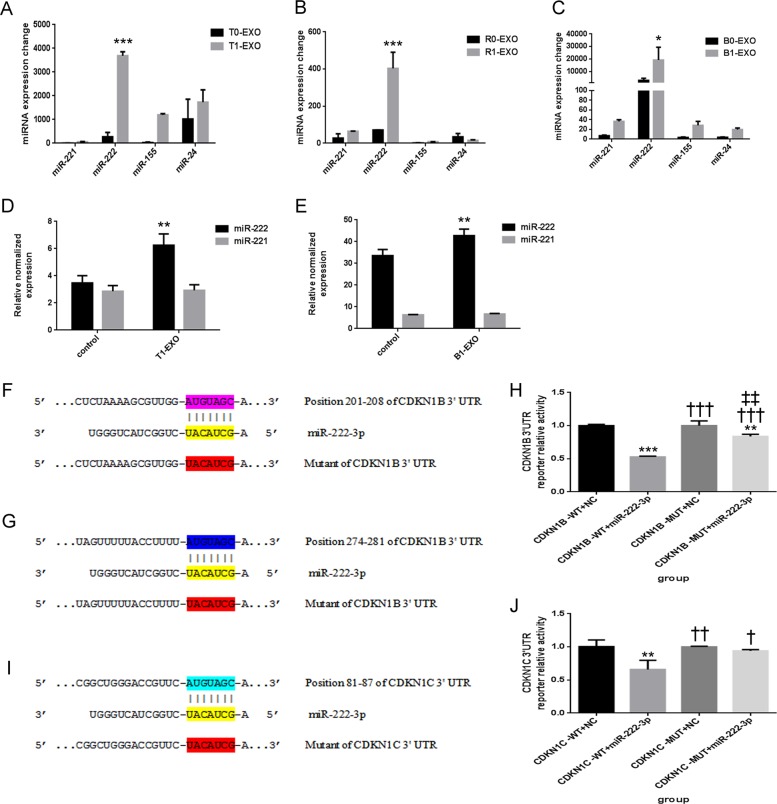
Fig. 3. Potential involvement of miR-222 in T1-EXO and direct target genes of miR-222.
a–c qPCR analysis of principal miRNAs that have been reported to play an important role in VSMCs functional changes. Four miRNAs (miR-221, miR-222, miR-155, and miR-24) were detected in exosomes from M0 macrophages and M1 macrophages, but only miR-222 was most significantly upregulated. *P < 0.05, versus exosomes from M0 macrophages group. n = 3, each group. d, e qPCR analysis of miR-222 expression in HA-VSMCs or primary VSMCs after incubation with T1-EXO or B1-EXO. *P < 0.05, versus control group. n = 3, each group. f, g Schematic representation of the putative binding sites in CDKN1B and CDKN1B mutant mRNAs 3′UTR for miR-222. h A luciferase reporter carrying the 3′UTR of CDKN1B (CDKN1B-WT) or mutant CDKN1B (CDKN1B-MUT) was introduced into 293T cells along with negative miR-control (NC) or miR-222-3p. Transfected cells were subjected to serum starvation for 48 h, and cell lysates were subjected to luciferase activity assay. *P < 0.05, versus CDKN1B-WT+NC group; †P < 0.05, versus CDKN1B-WT+miR-222-3p group; ‡P < 0.05, versus CDKN1B-MUT+NC group. n = 3, each group. i Schematic representation of the putative binding sites in CDKN1C and CDKN1C mutant mRNAs 3′UTR for miR-222. j A luciferase reporter carrying the 3′UTR of CDKN1C (CDKN1C-WT) or mutant CDKN1C (CDKN1C-MUT) was introduced into 293T cells along with negative miR-control (NC) or miR-222-3p. Transfected cells were subjected to serum starvation for 48 h, and cell lysates were subjected to luciferase activity assay. *P < 0.05, versus CDKN1C-WT+NC group; †P < 0.05, versus CDKN1C-WT+miR-222-3p group. n = 3, each group. All data were expressed as mean ± SEM from three individual experiments