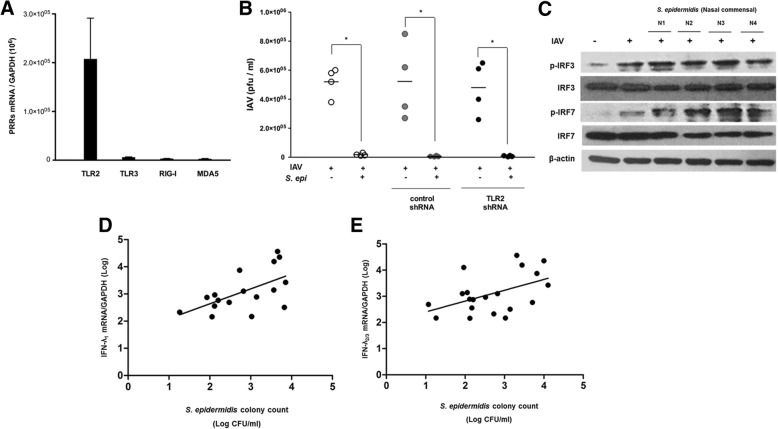
Fig. 3.
S. epidermidis induces interferon (IFN)-λ independently of pattern recognition receptors. a Abundance of transcripts encoding TLR2, TLR3, RIG-I, and MDA5 in normal human nasal epithelial (NHNE) cells infected with S. epidermidis 8 h before influenza A virus (IAV) infection was measured using real-time PCR at 1 day post-infection (dpi). b NHNE cells were transfected with control shRNA and TLR2 shRNA, and plaque assays were performed to measure viral titers of IAV-infected NHNE cells in the presence or absence of S. epidermidis. Results are presented as the mean ± SD from four independent experiments. *p < 0.05 compared to control NHNE cells. c IAV- and S. epidermidis-induced phosphorylation of IFN regulatory factor (IRF) 3 and IRF7 was assessed using western blot analysis. The mRNA levels of IFN-λ1 (d) and IFN-λ2/3 (e) in the nasal mucosa from middle turbinate of healthy volunteers (n = 17), as measured by real-time PCR, were correlated with the colony-forming units (CFUs) of S. epidermidis isolated from the mucus of the middle turbinate collected from the same subjects. The correlation was determined by Spearman’s correlation analysis