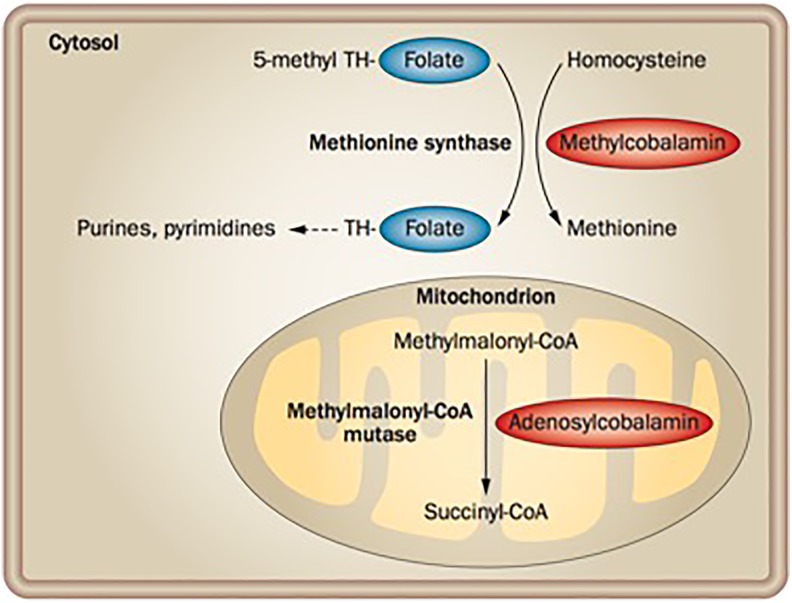
Figure 1.
Vitamin B12 coenzyme function. B12 acts as a coenzyme in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine in the cytosol, and the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in the mitochondrion. The cytoplasmic reaction requires folate, as the methyl group that is added to homocysteine is removed from 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate. Tetrahydrofolate is a precursor in the synthetic pathway for purines and pyrimidines, while succinyl-CoA enters the Krebs cycle and is important for lipid and carbohydrate synthesis. Reprinted with permission from Springer: Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology (Nielsen et al11).