Table 1.
Plant active ingredients effective on Parkinson’s disease.
| Name compound | Used model | Concentration | Effects | Chemical structures | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astragaloside IV | Cultures of primary nigral cells (PNCs) | 50, 100 and 200 µM | 1. Increased the level of TH and nitrite oxide synthase (NOS) immune reactivities 2. Protect dopaminergic neurons degeneration 3. Promoted neurite outgrowth and increased TH and NOS immune reactive of dopaminergic neurons |
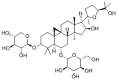 |
Chan et al. (2009) |
| Berberine | 1. 6-OHDA induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells 2. Unilateral 6-OHDA-lesioned rats |
5, 10 and 30 µM | 1. Depleted tyrosine hydroxylase-immuno positive cells in the substantia nigra 2. Decreased dopamine and norepinephrine levels in striatal regions |
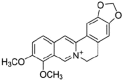 |
Kwon et al. (2010) |
| Baicalein | 6-OHDA induced in vitro and in vivo | 0.5, 5 μg/mL | 1. Ameliorate SH-SY5Y cell apoptosis 2. Promote neurite outgrowth of PC12 cell 3. Attenuate muscle tremor 4. Increase tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive neurons |
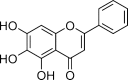 |
Mu et al. (2009) |
| Caffeic acid phenethyl ester | In vitro (cerebellar granule neurons) | 10 µm | 1. Modulate the Ca2+-induced release of cyctochrome c 2. Inhibit caspase-3 activation 3. Blocks cell death |
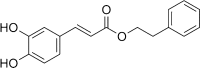 |
Noelker et al. (2005) |
| Carnosic acid | Rat induced by 6-OHDA | 20 mg/kg | 1. Improved the locomotor activity 2. Reduced the apomorphine-caused rotation 3. Reduced lipid peroxidation 4. GSH reduction 5. Increased the protein expression of c-glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione reductase 6. Reduction of the Bcl-2/Bax ratio 7. Induction of caspase 3 cleavage 8. Induction of poly (ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage |
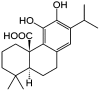 |
Wu et al. (2015) |
| Curcumin | Rat induced by 6-OHDA | 80 mg/kg pretreatment | 1. Decreased MDA, 2. Increased glutathione, GPx, glutathione reductase, SOD, catalase, tyrosine hydroxylase and D2 receptor binding in brain tissue |
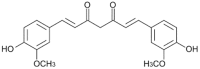 |
Khuwaja et al. (2011) |
| Gallic acid | Rat induced by 6-OHDA | 50, 100 and 200 mg/kg | 1. Increased the passive avoidance memory 2. Increased total thiol in brain tissue 3. Increased GPx 4. Decreased MDA levels in brain tissue |
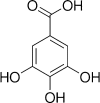 |
Mansouri et al. (2013) |
| Ellagic acid | Rat induced by 6-OHDA | 50 mg/kg | 1. Increased of stride-length 2. Decreased the contralateral rotations 3. Decreased TNF-α and IL-1β levels in brain tissue |
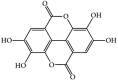 |
Farbood et al. (2015) |
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | (6-OHDA) induced neurotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells | 0.01 µM | 1. Increased survival 2. Rescue occurred on cell viability 3. Restore the up-regulation of Bax and down-regulation of Bcl-2 mRNA and protein expression 4. Attenuate 6-OHDA-induced apoptosis |
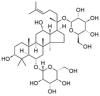 |
Gao et al. (2009) |
| Quercetin | Rat induced by 6- OHDA | 50 mg/kg | 1. Increased dopamine 2. Decreased protein carbonyl content |
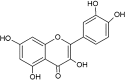 |
Haleagrahara et al. (2013) |
| Desferrioxamine | Rat induced by 6-OHDA | 50 mg/kg | 1. Decreased protein carbonyl content 2. Increased dopamine, GSH and SOD levels |
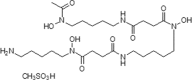 |
Haleagrahara et al. (2013) |
| Thymoquinone | Rat induced by 6- OHDA | 5, 10 mg/kg | 1. Improved turning behaviour 2. Decreased MDA levels 3. Increased activity of superoxide dismutase 4. Prevented loss of SNC (substantia nigra pars compacta) neurons |
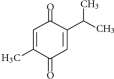 |
Sedaghat et al. (2014) |
| Tripchlorolide | (MPTP)-lesioned C57BL/6 mice | 1 µg/kg | 1. Increased level of dopamine in the substantia nigra and striatum | 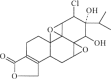 |
Hong et al. (2007) |
| Sulforaphane | mice induced by 6-OHDA | 5 mg/kg | 1. Improved motor coordination 2. Blocking DNA fragmentation and caspase-3 activation 3. Increased glutathione levels |
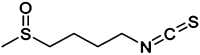 |
Morroni et al. (2013) |
