Figure 1. Meiosis and crossover formation.
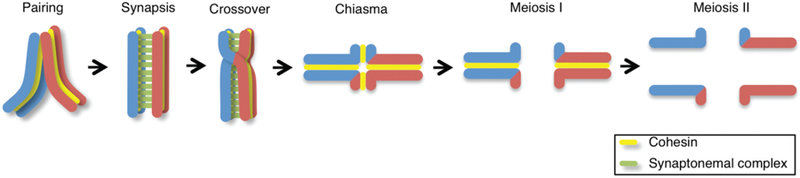
Chromosome dynamics during meiosis. After premeiotic DNA replication, homologous chromosomes find each other (pairing) during the leptotene-zygotene stages. The synaptonemal complex assembles, aligning and holding homologs together throughout their full lengths (synapsis) at the pachytene stage. Repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) via crossover formation involves the reciprocal exchange of genetic information between homologs. A chiasma is the cytologically visible manifestation of an earlier crossover event underpinned by flanking sister chromatid cohesion and is observed as a cruciform configuration during the diplotene to diakinesis transition. Homologous chromosomes are segregated at the metaphase I to anaphase I transition and sister chromatids are separated at the metaphase II to anaphase II transition. Paternal chromatids are blue and maternal chromatids are red. Sister chromatid cohesion is depicted in yellow and the synaptonemal complex is depicted in green.
