Figure 2. Model of homologous recombination.
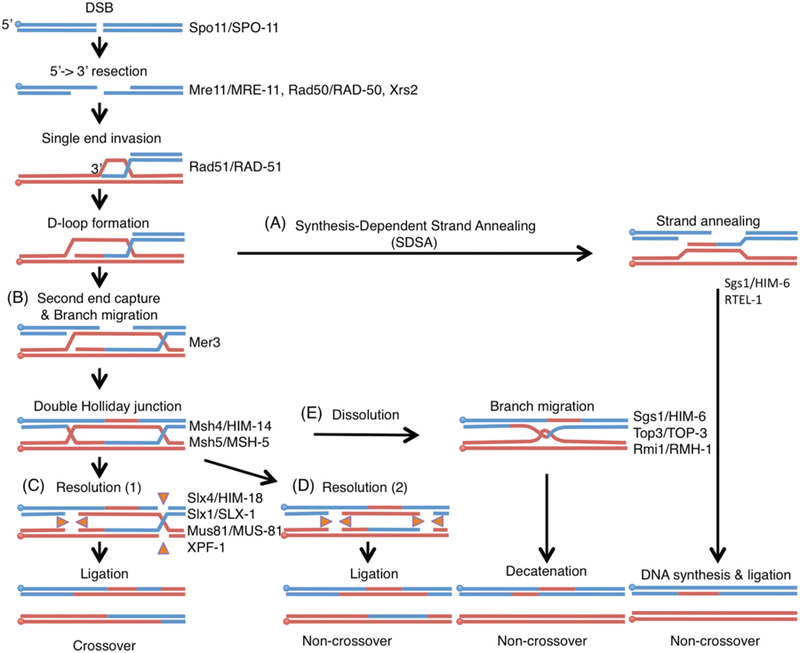
DNA double strand breaks are generated by the topoisomerase-like protein Spo11. The MRN/X complex (Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1/Xrs2) resects the 5’ends to expose 3’overhangs. Single end invasion (SEI) is mediated by Rad51. Homologous recombination can then proceed through the following pathways: (A) synthesis-dependent strand annealing resulting in non-crossover products or (B) double Holliday junction (dHJ) formation by Mer3 and Msh4-Msh5 resulting in crossover (CO) formation. The DNA helicase ReqQ homologs Sgs1 and RTEL-1 disrupt D-loops to anneal both ends of the DSB. Once double Holliday junctions are formed, they are resolved by the structure-specific endonucleases SLX-1-SLX-4/HIM-18, MUS-81-EME1 and XPF-ERCC1. (C) Asymmetric resolution of the dHJ produces crossovers and (D) symmetric resolution results in non-crossovers. (E) dHJs can also be processed by the dissolution pathway through the BTR complex (BLM-TOP3-RMI1/2) to make non-crossover products. Paternal DNAs are blue and maternal DNAs are red. Circles indicate 5’side of DNA. Orange triangles indicate the direction of catalytic activities of Holliday junction resolvases. Key proteins acting at each step are indicated on the right and both yeast and worm names are indicated.
