Figure 4. Tight regulation of crossover formation in C. elegans.
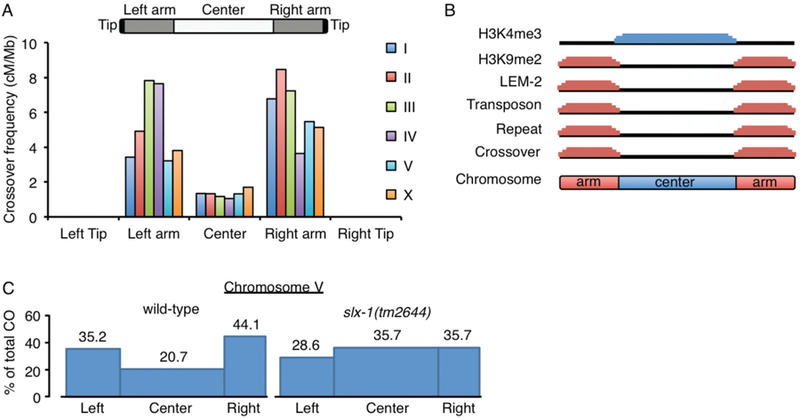
(A) Crossovers are enriched at arm regions but suppressed at center regions in both autosomes and the X chromosome in C. elegans. No crossovers are observed at subtelomeric regions (average <614kb from telomeres). Data was adapted from (Rockman and Kruglyak 2009). (B) Unique features divide chromosome domains in C. elegans. Although up to ~10 DSBs are distributed in a non-biased manner along chromosomes (Saito et al. 2012), crossovers occur at the arm regions where the heterochromatin marker histone H3K9me2, the nuclear membrane protein (LEM-2) binding sequences, transposons, and repeat sequences, are enriched. Crossover formation is suppressed at the center region where the euchromatic marker histone H3K4me3 is enriched. (C) Crossover suppression at the center region of autosomes is lost in slx-1(tm2644) null mutants. Blue boxes indicate crossover frequencies (Saito et al. 2012). While the overall crossover frequency is not altered, crossover distribution is altered by increasing at the center region and decreasing at the arms in slx-1 mutants compared to wild type.
