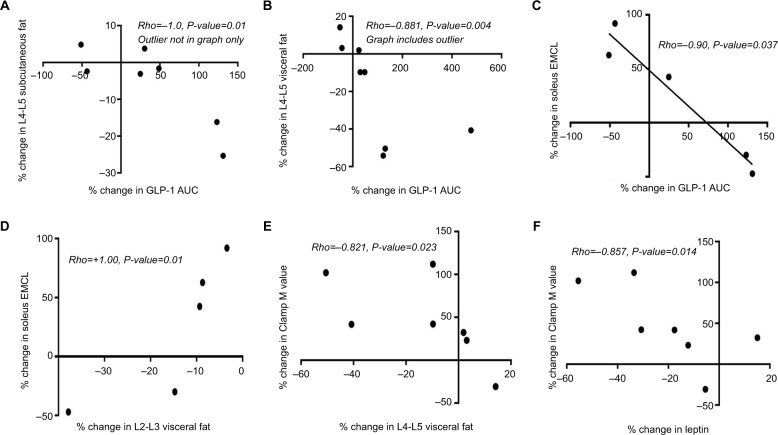
Figure 1.
Spearman correlation demonstrating the significant associations among percentage changes in GLP-1 hormone and visceral adiposity in the leg skeletal muscle and in the abdomen, peripheral insulin sensitivity and leptin (A–F). Roflumilast induced alteration of insulin sensitivity is associated with changes in leptin (F) and in visceral adiposity (E).
Notes: In this small study, the association of changes in GLP-1 AUC with changes in adiposity (A–C) suggests that roflumilast’s early effects on insulin sensitivity may be through reduction in adiposity and/or through incretin effect. Roflumilast-induced association between changes in soleus EMCL and L2-L3 visceral fat (D) highlights possible linkage between these two anatomically separate, visceral fat depot.
Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; EMCL, extramyocellular lipid; GLP, glucagon-like peptide.