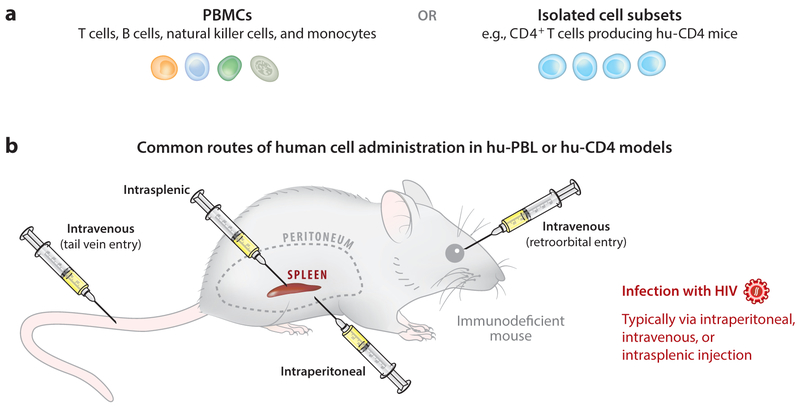
Figure 1.
The human peripheral blood leukocyte (hu-PBL) and hu-CD4 models. (a) Implanted human primary cells are most often peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or isolated CD4+ T cells. These cells might be derived from healthy donors if the mouse is to be subsequently infected with virus, or from HIV-infected individuals if analysis of patient-derived cells or outgrowth of new primary virus isolates is desired. (b) Humanization of immunodeficient mice can be achieved by injecting mature cells through one or more of several different routes, but it is most commonly performed through intraperitoneal or intravenous injection. Infection with HIV is also generally performed through these same routes.