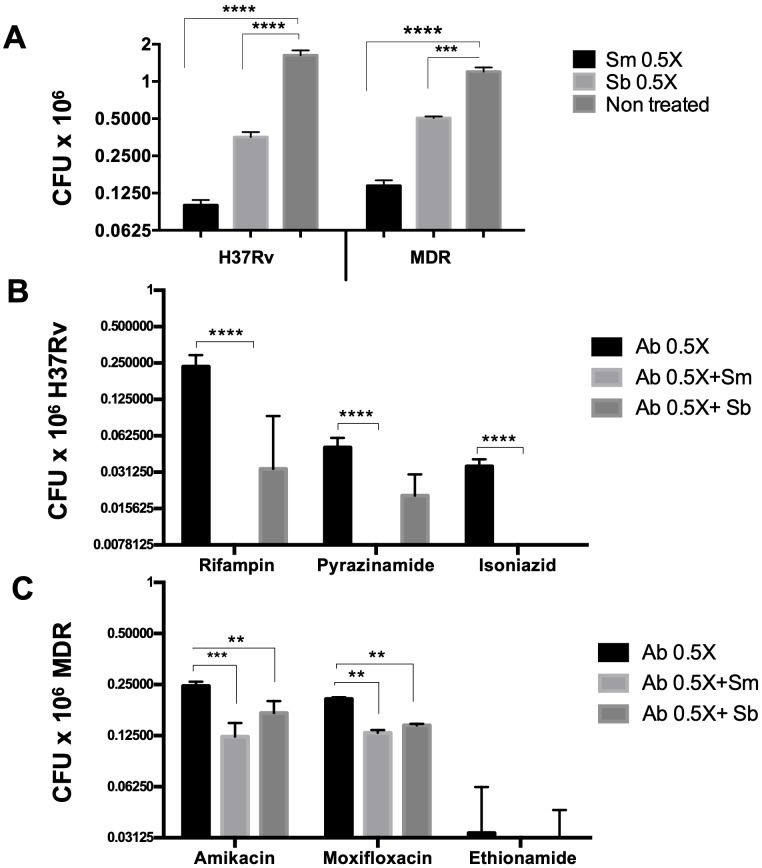
Fig 3. Determination in vitro of the synergistic activity of silymarin (Sm) and silibinin (Sb) with antituberculous drugs.
The Sm and Sb antimicrobial activity was determined by CFUs (A) using the MIC determination. The viability determined by CFUs of the M. tuberculosis H37Rv (B) or MDR strain (C) was evaluated by using the half MIC concentration (0.5X) of the first- and second-line antibiotics. Dose 0.5X: rifampicin (0.05 μg/ml), pyrazinamide (2.8 μg/ml), isoniazid (0.05 μg/ml), amikacin (2 μg/ml), ethionamide (2.6 μg/ml), and moxifloxacin (2 μg/ml), respectively, in the presence or absence of 30 μg/ml of Sm or Sb (Ab 0.5X+Sm/Sb). Using half of the recommended dose (0.5X), the bacteria were eliminated more efficiently in the presence of either flavonoid, with Sm being more efficient than Sb. Data represent the mean ± SEM of four independent determinations p ≤ 0.05.