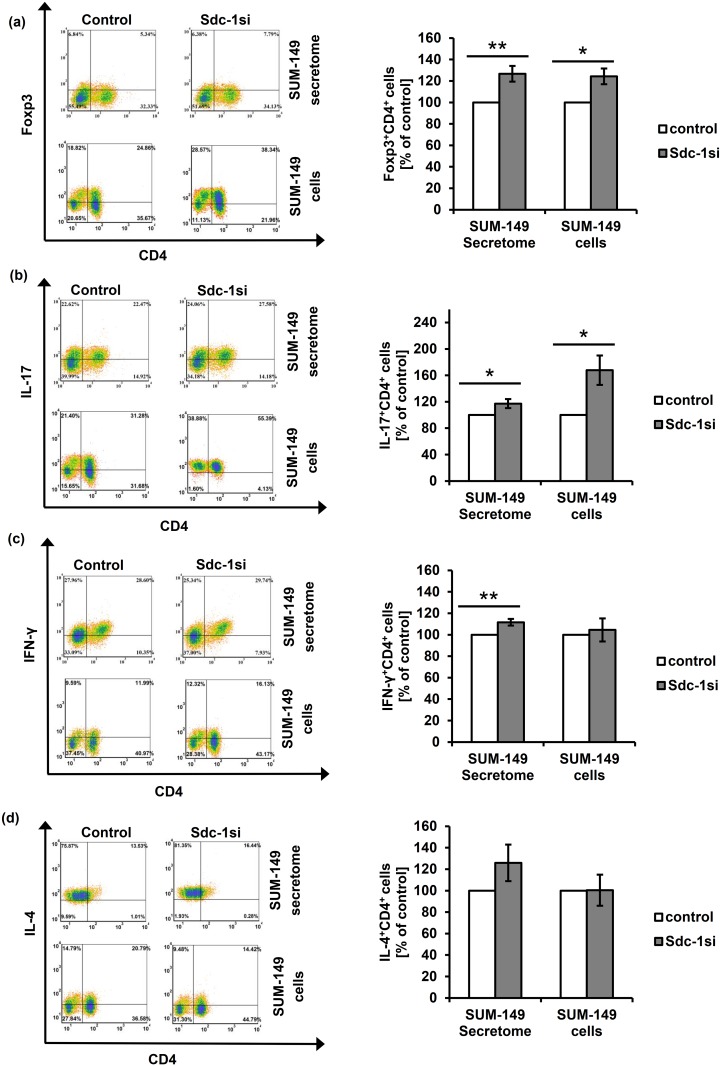
Fig 2. Effect of tumor Sdc-1 silencing on the polarization of T helper subsets of non-IBC patients.
Lymphocytes isolated from axillary blood of non-IBC patients were either stimulated by the secretome of control and Sdc-1-silenced SUM-149 cells for 96 h or directly co-cultured with control and Sdc-1-silenced SUM-149 cells for 48 h. Lymphocytes were then stained with labeled antibodies against CD4-FITC, IFN-γ-PE, IL-4-PEcy7, IL-17-PE, and Foxp3-PEcy7. Relative to control cells, both Sdc-1-silenced SUM-149 cells and their secretome enhance (a) Treg (Foxp3+CD4+) and (b) Th17 (IL-17+CD4+) subsets, whereas only the secretome of Sdc-1-silenced SUM-149 cells augments (c) the Th1 (IFN-γ+CD4+) subset. No effect of Sdc-1 silencing in SUM-149 cells on (d) the Th2 (IL-4+CD4+) subset was detected upon stimulation with their secretome or in co-culture. Left panels of (a-d) are representative flow cytometric analyses of CD4+ T cell subsets. Data shown is representative for a single experiment. Right panels of (a-d) show the quantification of CD4+ T cell subsets as analyzed by flow cytometry. Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 15 for samples stimulated by the secretome of SUM-149 cells, and n = 5 for samples co-cultured with control and Sdc-1-silenced SUM-149 cells. * P ≤ 0.05, ** P ≤ 0.01 as determined by Student’s t test.