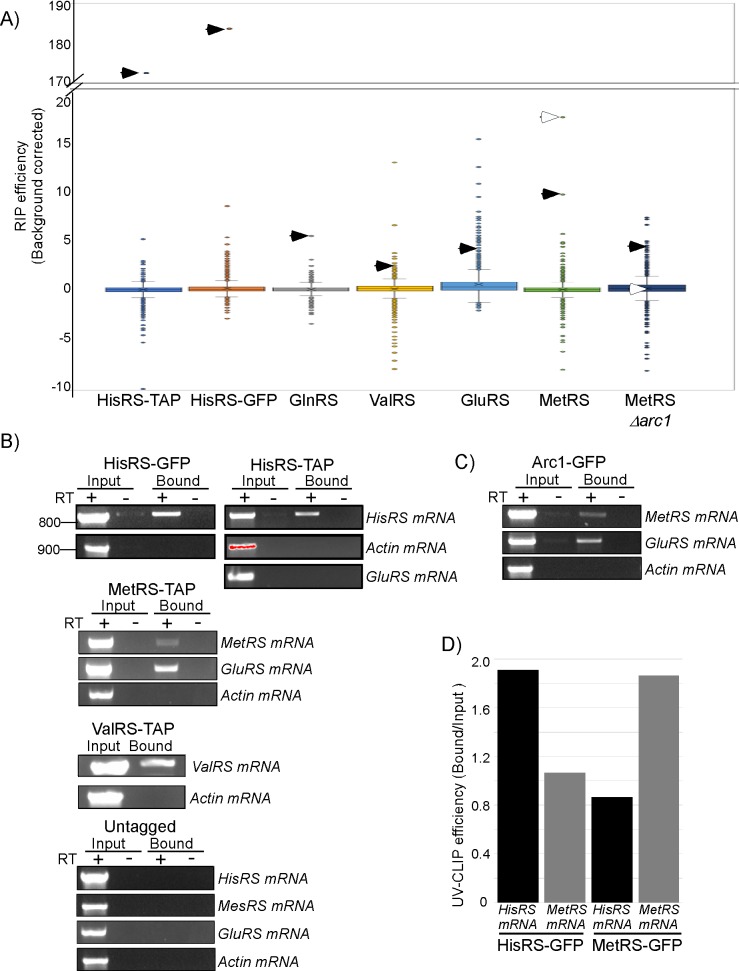
Fig 1. mRNA binding by aaRSs.
A) Yeast strains expressing the indicated tagged aaRS (either TAP or GFP tagged) or an untagged control strain were subjected to RIP-seq analysis. The box plot presented the RIP efficiency (calculated as RPM in the Bound sample divided by RPM in the Input) corrected for background (i.e., subtracted by the RIP efficiencies obtained by the untagged strain RIP-seq) from a single experiment. Extreme values are presented by circles, and whiskers correspond to 1.5 IQR. Closed arrowheads point the position of the mRNA encoding the respective aaRS. Open arrowheads point the mRNA encoding GluRS. See S2 Table for complete data set. B) Semiquantitative RT-PCR confirmation of positive hits. RNA was extracted from either the Input sample or the Bound RNA and subjected to reverse transcription either with (+) or without (-) the RT enzyme. cDNA was subjected to PCR with primers specific to the indicated genes, and products were collected every five cycles and resolved on an agarose gel. Representative gel images from the same PCR cycle are presented. Data are representative of two independent biological repeats. Red shading for the Actin signal in the Input sample of HisRS-TAP indicates saturation. C) Semiquantitative RT-PCR for RIP analysis of Arc1-GFP strain. D) Quantitative RT-PCR for the indicated mRNAs, isolated by UV cross-linking, followed by IP from HisRS-GFP and MetRS-GFP strains. Results are presented as the ratio between Bound and Input RT-qPCR signals and are representative of two independent biological repeats. Raw data is presented in S6 Table. aaRS, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; GFP, green fluorescent protein; GluRS, glutamyl-tRNA synthetase; HisRS, histidyl-tRNA synthetase; IP, immunoprecipitation; IQR, InterQuartile Range; MetRS, methionyl-tRNA synthetase; RIP, RNA immunoprecipitation; RPM, reads per million; RT-PCR, reverse transcription PCR; TAP, Tandem Affinity Purification.