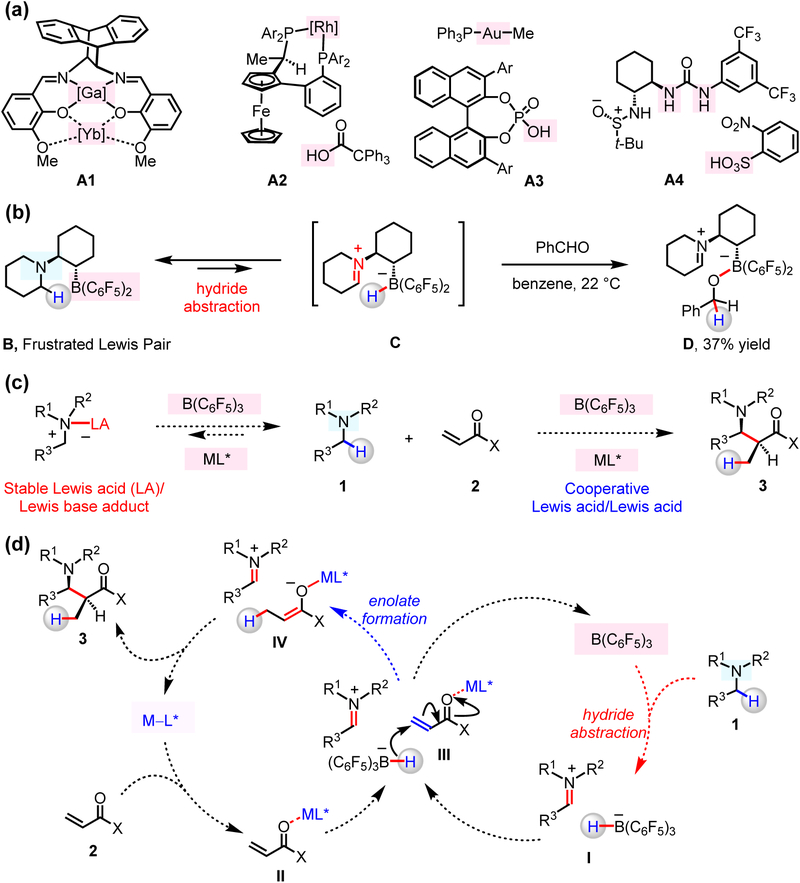
Figure 1. Structures and reactivity of cooperative catalysts.
(a) Previously reported examples of cooperative acid/acid catalysts involve structurally and/or functionally disparate acidic promoters. (b) Intramolecular hydride transfer occurs within a frustrated Lewis pair complex to afford zwitterionic iminium ions. (c) Enantioselective coupling of N-alkylamines and α,β-unsaturated compounds by cooperative acid/acid catalysis. (d) A possible mechanism might involve enantio- and diastereoselective C–C bond formation between iminium ion and chiral enolate, generated in situ by cooperative functions of a chiral and an achiral Lewis acid catalyst. The reaction affords β-amino carbonyl compounds atom economically and under redox neutral conditions.