Figure 1. LISP2 marks the beginning of hepatic stage development.
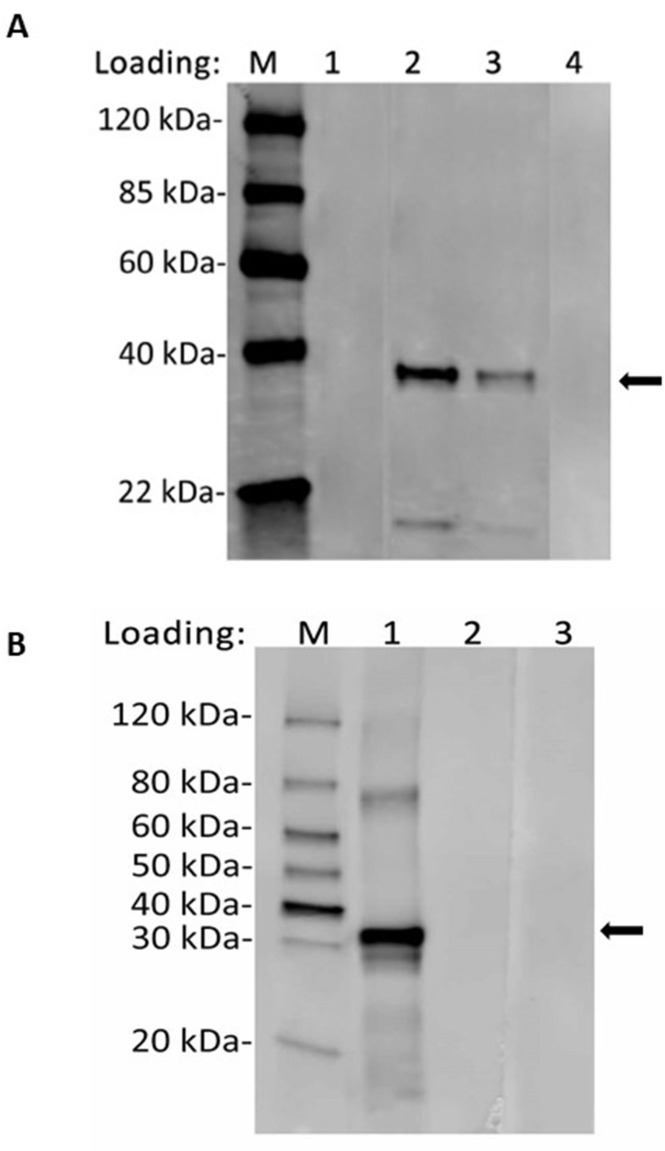
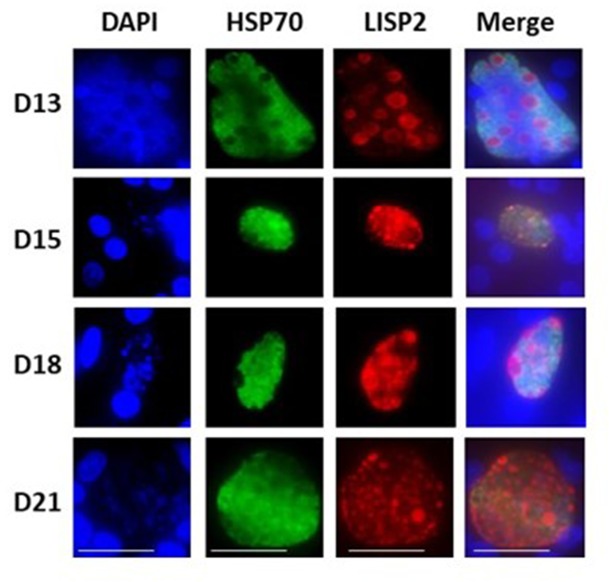
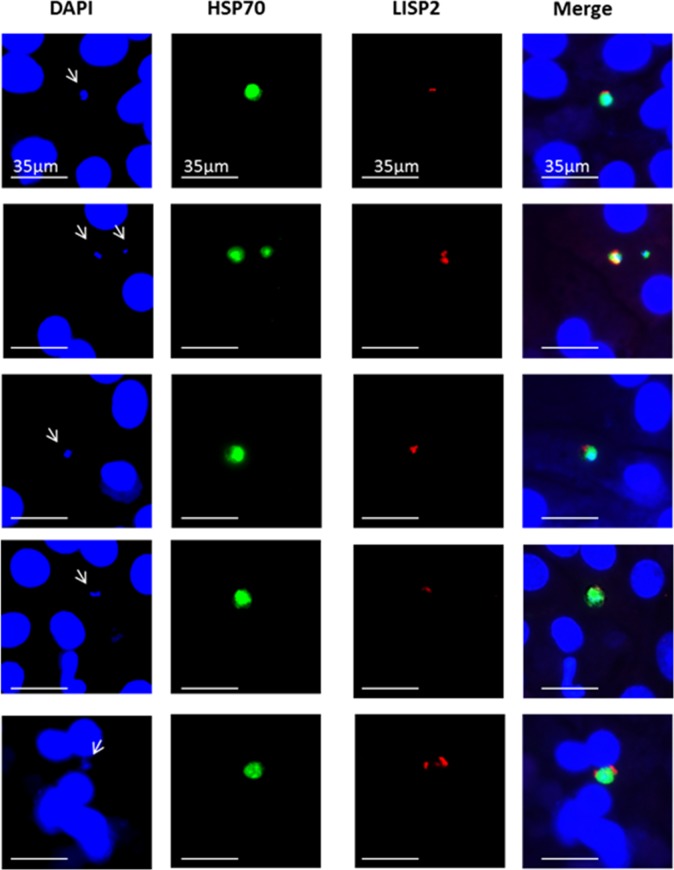
(A) Schematic structure of the LISP2 gene showing the N-terminal signal peptide, 6-cys domain and epitope (highlighted in black) used as immunogen to raise antibodies against P. cynomolgi and P. vivax LISP2 protein (B) Immunofluorescence assay, IFA of P. cynomolgi liver stage parasites in infected simian primary hepatocytes showing liver stage development from day 1 to day 12 post-infection visualized with DAPI for DNA content (blue), a polyclonal antibody specific for P. cynomolgi HSP70 protein (green) and a monoclonal antibody specific for P. cynomolgi LISP2 protein (red); Scale bar, 35 µm. From day 3 onwards, LISP2 staining observed in a crescent shape asymmetrically located on one side of earliest developing parasites (LISP2+). By day 5, LISP2 accumulates in peripheral vacuolar membrane structures in multinucleate schizonts and does not co-localize with DAPI or HSP70 (LISP2++).