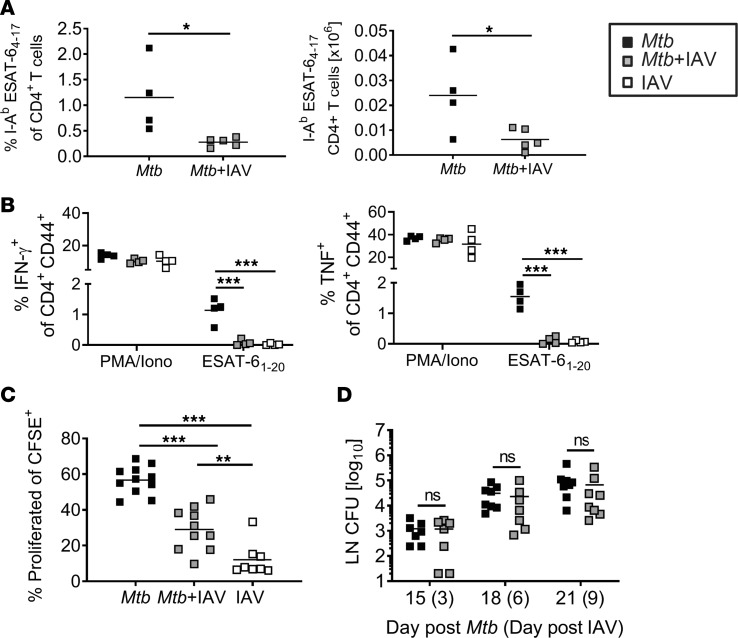
Figure 4. Impaired priming of Mtb-specific CD4+ T cells in dLNs in coinfected mice.
C57BL/6 mice were infected via aerosol with a low dose of Mtb H37Rv and 12 days later coinfected i.n. with 1 × 104 PFU IAV (A/HH/05/09 H1N1). dLNs were collected 9 days after IAV (co)infection (day 21 Mtb) and analyzed by flow cytometry for the presence of (A) I-Ab ESAT-64–17–specific CD4+ T cells (n = 4–5 per group, representative of 2 independent experiments) and (B) IFN-γ– and TNF- producing CD4+ T cells upon ex vivo restimulation with PMA/Iono or ESAT-61–20 peptide (n = 4 per group, representative of 2 independent experiments). (C) dLNs from mice that received CFSE-labeled CD4+ T cells from P25TCR-tg mice were collected at day 21 Mtb (day 9 IAV) and analyzed for the proportion of proliferated CD4+ T cells by flow cytometry (n = 8–11 per group, representative of 2 independent experiments). (D) dLNs were collected at indicated time points and analyzed for bacterial burden (n = 7–8 per group, pooled data from 2 independent experiments). Each data point represents 1 mouse. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 determined by (A and D) unpaired t test and (B and C) 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test.