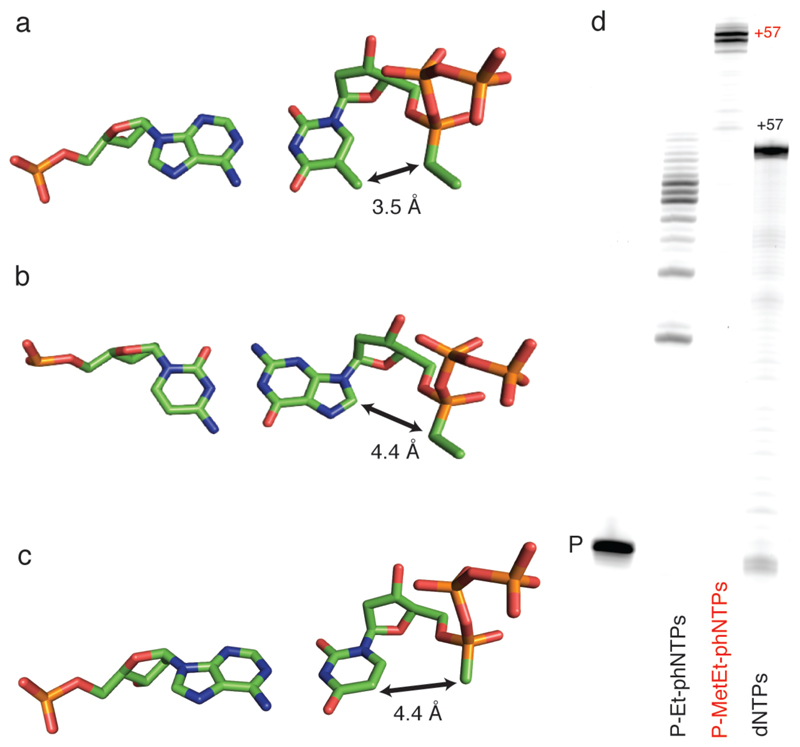
Figure 4. Structural context of Sp P-alkyl-phNTP incorporation.
A) Structure of a model of the polymerase active site based on the ternary complex structures of RB69 polymerase (PDB: 3CFP, PDB 4FJH). The estimated distance between the C5-methyl and P-ethyl groups (assuming no conformational adjustments) is shown for A) Sp P-Et-phTTP : dA pair; for B) between C5 and P-methyl group of the Sp P-Met-phUTP: dA pair and compared C) between C8 and P-ethyl group for the Sp P-Et-phGTP : dC pair. Note that P-Met-phU : dA shows similar distance as P-Et-phG:dC pair. D. PAGE of primer extension on an unbiased template TempN (Supplementary Table 5) showing synthesis of using P-Et-phNTPs with multiple pausing (mostly corresponding to template dApdA) or full-length synthesis of using P-MetEt-phNTP mix by PGV2 (P: unextended primer). Note the reduced electrophoretic mobility of full-length phNA (57 nt) compared to DNA control (57 nt).