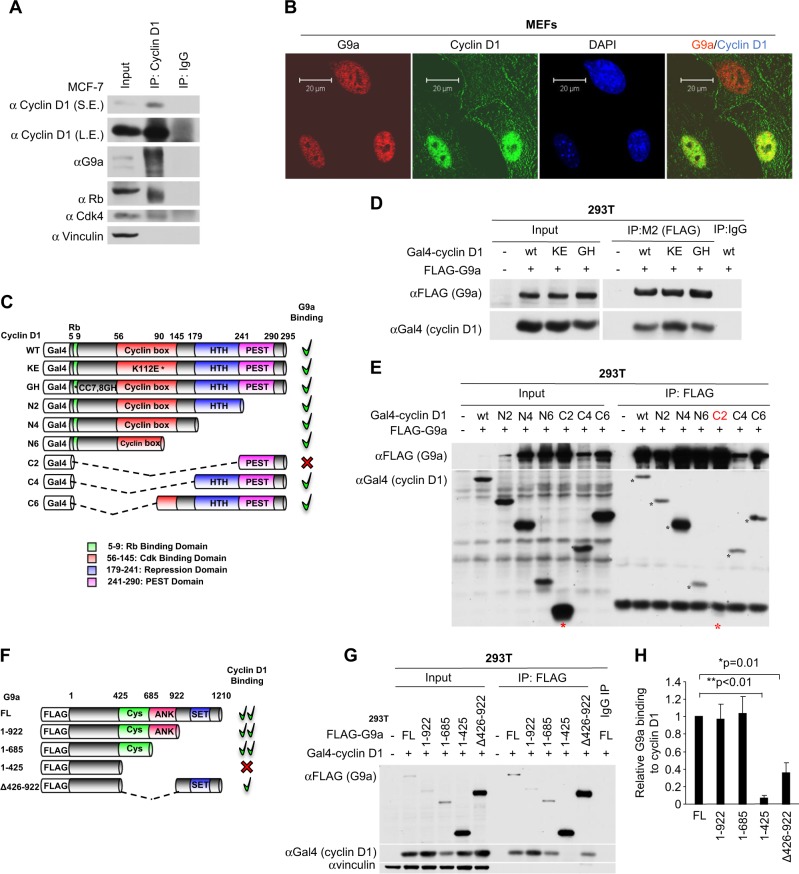
Fig. 1.
Cyclin D1 binds G9a. a Cyclin D1 immune-precipitation was conducted in MCF-7 cells, with subsequent western blotting to the proteins indicated. b Confocal microscopy of immunofluorescence for G9a (red), cyclin D1 (green), and nuclear staining with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue) in cyclin D1+/+ mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). Scale bar, 20 μm. c Schematic representation of GAL4-tagged cyclin D1 expression vectors with relative G9a binding. d Immunoprecipitation using an antibody to the FLAG-tag of G9a with sequential western blot to the GAL4 for GAL4-cyclin D1 in 293T cells co-transfected with FLAG-tagged G9a and GAL4-tagged cyclin D1 wild type, KE mutant, and GH mutant. e Immunoprecipitation using an antibody to the FLAG-tag of G9a and sequential western blotting to GAL4 for GAL4-cyclin D1 wild type and truncation mutants. Note the relative abundance of C2 and C4 in the input and lack of cyclin D1 in C2 but not in C4 by FLAG immunoprecipitation (IP)-western blot. f Schematic representation of FLAG-tagged G9a expression vectors with relative cyclin D1 binding. g IP-western after precipitation with anti-FLAG antibody for FLAG-tagged G9a in sequential western blotting to the GAL4 for GAL4-cyclin D1 in 293T cells co-transfected with GAL4-tagged cyclin D1 and FLAG-tagged G9a wild type and truncation mutants. h Quantitation of FLAG-tagged G9a binding to GAL4-tagged cyclin D1 in 293T cells from three independent experiments. The binding amount of FLAG-tagged wild-type G9a to GAL4-tagged cyclin D1 in each experiment was set as 1. The data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P = 0.01; **P < 0.01 (n = 3)