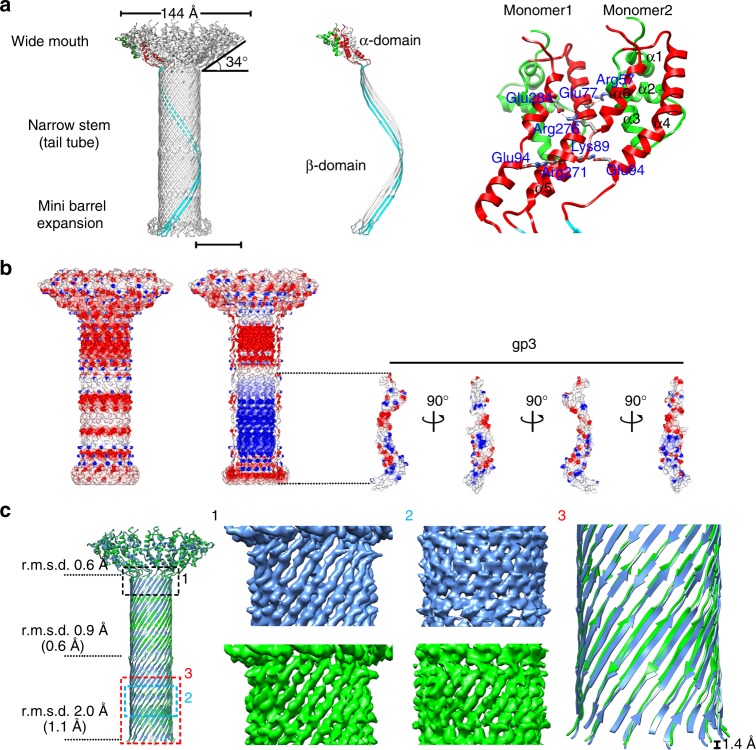
Fig. 7.
Structure of the lower collar. a Left: Ribbon diagrams showing the lower collar assembly; middle: ribbon diagrams showing two gp11 monomers of the lower collar assembly. One of the two monomers is colored according to its domains (gp11-α1–3: green, gp11-α4–6: red, β-domain: cyan), while the other gp11 monomer is colored gray; right: a zoom-in showing salt bridges in between two gp11 monomers at the wide mouth region of the funnel-shaped lower collar. The scale bar represents 5 nm. b Surface electrostatic potential of the lower collar and the terminal protein gp3. Negative and positive electrostatic potentials are colored red and blue, respectively. Left: outer surface electrostatic potential of the lower collar; middle and right: inner surface electrostatic potential of the lower collar and outer surface electrostatic potential of the terminal protein gp3. c Left: ribbon diagrams showing gp11 α-domain-based structural superimpositions of the mature virion lower collar (blue) and the genome emptied virion lower collar (green). R.m.s.d.s for different portions of the lower collar were calculated and shown at the left side of the superimposition. The r.m.s.d.s shown in the parentheses were calculated from the structural superimpositions by using the upper or the bottom portion of the β-domain; middle: representative densities of the upper and the bottom portions of the β-domains; right: a zoom-in showing the contraction of the lower collar upon genome release