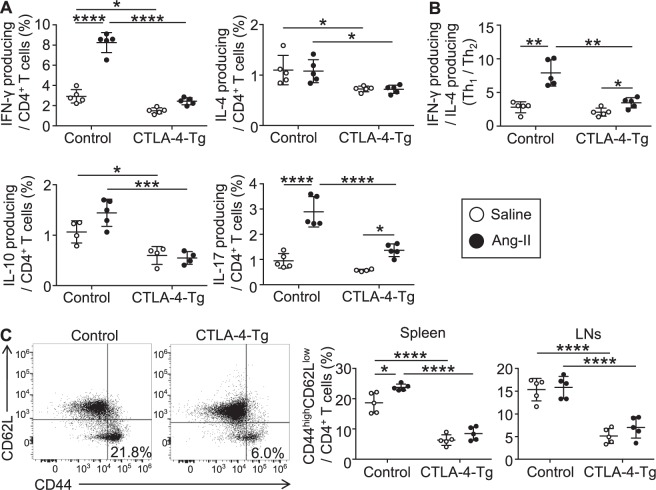
Figure 4.
Overexpression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) suppresses systemic T cell immune responses in angiotensin II-treated or saline-treated mice. Seven days after the pump implantation, lymphoid cells from spleen and lymph nodes (LNs) were prepared. Apolipoprotein E-deficient (Apoe−/−) mice infused with angiotensin II or saline served as controls. (A) The graphs represent the frequencies of interferon (IFN)-γ+, interleukin (IL)-4+, IL-10+, and IL-17+ CD4+ T cells in the spleen of each group. n = 5 per group. (B) The ratio of IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells to IL-4+ CD4+ T cells was determined as T helper type 1 (Th1)/Th2 ratio. n = 5 per group. (C) Representative results of CD44 and CD62L expression in splenic CD4+ T cells of angiotensin II-infused Apoe−/− and CTLA-4-Tg/Apoe−/− mice assessed by flow cytometry. The graphs represent the percentage of CD44highCD62Llow effector T cells within the spleen and LN CD4+ population. n = 5 mice per group. Data points represent individual animals. Horizontal bars represent means. Error bars indicate s.d. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Ang-II, angiotensin II.