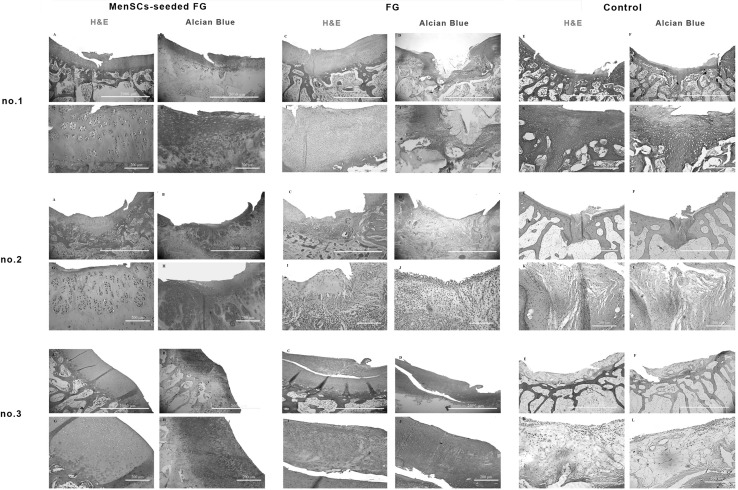
Fig. 4.
Microscopic appearance of the repaired cartilage defects at 3 months in three selected samples from each group (H and E and Alcian blue staining); (no.1 A, no.2 A, no.3 A): (FG + MenSCs group), the defects were filled with hyaline cartilage-like tissue. (no.1 G, no.2 G, no.3 G): higher magnification of previous slides, note to well-differentiated chondrocyte-like cells within lacunae with isogenic and/or columnar pattern. (no.1 B, no.2 B, no.3 B): intense staining of alcian blue staining in FG + MenSCs group indicted noticeable amount of proteoglycans. (no.1 H, no.2 H, no.3 H), higher magnification of previous slides. (no.1 C, no.2 C, no.3 C): (FG group), the defects were mostly filled with fibrocartilage and fibrous repair tissues. (no.1 I, no.2 I, no.3 I): higher magnification of previous slides, note to fibrocartilaginous tissue with disorganized chondrocyte. (no.1 D, no.2 D, no.3 D): The alcian blue staining exhibited variable intensity in FG group. (no.1 J, no.2 J, no.3 J): higher magnification of previous slides. (no.1 E, no.2 E, no.3 E): (control group), the defect was mainly filled with fibrocartilaginous repair tissue with infiltration to subchondral bone portion (no.1 E). In (no.2 E, no.3 E), the defects showed spontaneous healing and were mainly covered by an immature fibrous tissue. (no.1 K, no.2 K, no.3 K): higher magnification of previous slides. (no.1 F, no.2 F, no.3 F): the extra cellular matrixes of cases belonged to the control group showed slight to moderate intensity of alcian blue staining. (no.1 L, no.2 L, no.3 L): higher magnification of previous slides