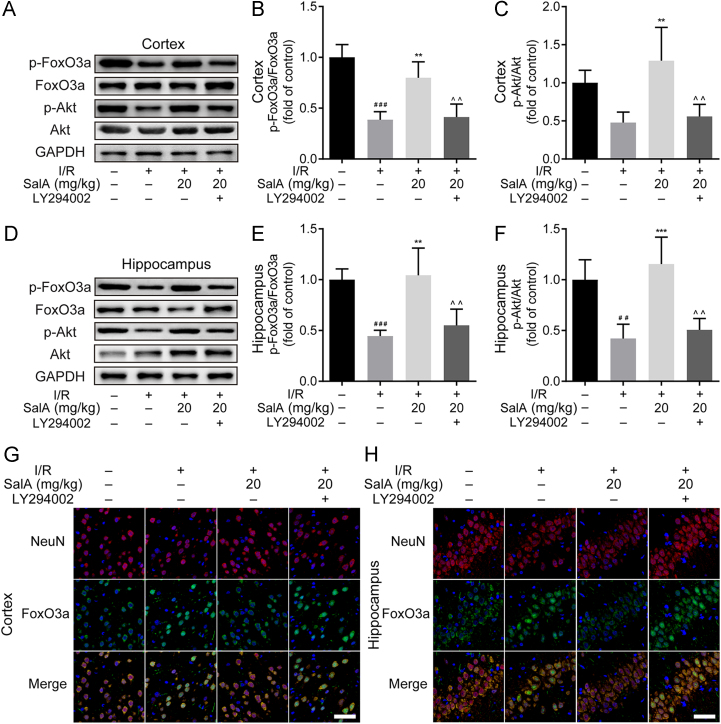
Figure 5.
SalA inhibited MCAO/R injury induced FOXO3a nuclear translocation and upregulated AKT phosphorylation in rat brain cortex and hippocampus. (A) The levels of p-FOXO3a, FOXO3a, p-AKT and AKT in rat brain cortex treated by SalA without or with LY294002. (B) The p-FOXO3a/FOXO3a ratio in rat brain cortex treated by SalA without or with LY294002. (C) The p-AKT/AKT ratio in rat brain cortex treated by SalA without or with LY294002. (D) The levels of p-FOXO3a, FOXO3a, p-AKT and AKT in rat brain hippocampus treated by SalA without or with LY294002. (E) The p-FoxO3a/FoxO3a ratio in rat brain hippocampus treated by SalA without or with LY294002. (F) The p-AKT/AKT ratio in rat brain hippocampus treated by SalA without or with LY294002. (G) The expression and localization of FOXO3a (green fluorescence) and NeuN (red fluorescence) in rat brain cortex treated by SalA without or with LY294002 by immunofluorescence assay. (H) The expression and localization of FOXO3a (green fluorescence) and NeuN (red fluorescence) in rat brain hippocampus treated by SalA without or with LY294002 by immunofluorescence assay. Data was expressed as mean±SD of 4 independent tests. ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 compared with sham group, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with I/R group, ^^P<0.01 compared with I/R+SalA group. Scale bar=50 μm.