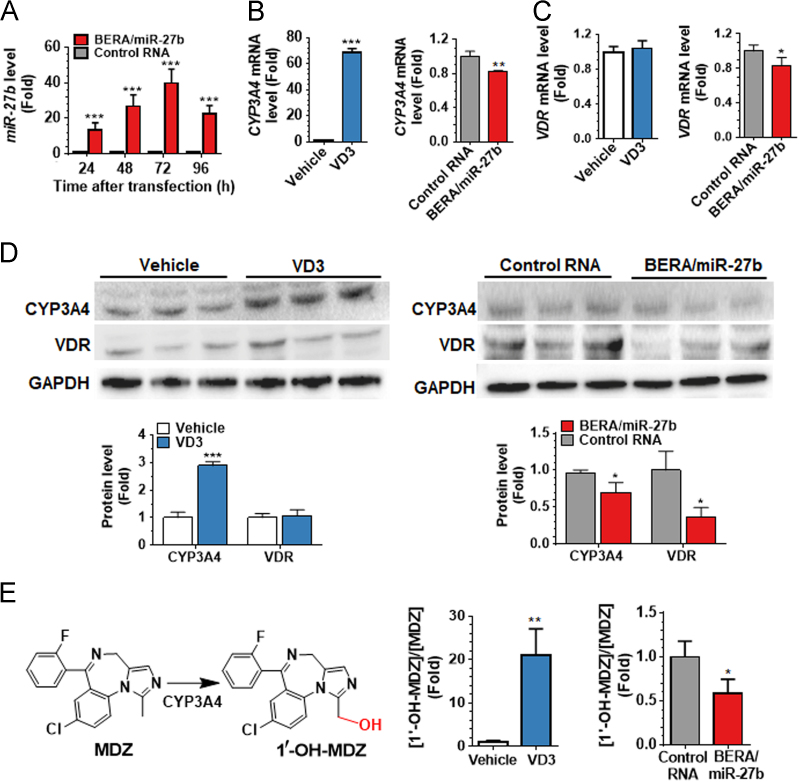
Figure 2.
BERA/miR-27b-3p is processed to miR-27b-3p in human LS-180 cells, effectively reduces VDR and CYP3A4 protein expression levels, and thus alters cellular CYP3A4 drug metabolism capacity. LS-180 cells was transfected with 50 nmol/L BERA/miR-27b-3p or control RNA for 24, 48, 72 and 96 h. Levels of miR-27b-3p in BERA/miR-27b-3p treated cells were significantly higher than control RNA and the high level of miR-27b-3p persisted 96 h (A). Treatment of 1α-VD3 greatly induced CYP3A4 mRNA (B) and protein (C) expression, whereas had no effect on VDR mRNA (B) or protein (C) levels. Following the induction by 1α-VD3, CYP3A4 (B) and VDR (C) mRNA levels, as well as their protein levels (D) were significantly reduced by BERA/miR-27b-3p, compared to control RNA (C). CYP3A4 enzymatic activity, as measured by [1′-OH-MDZ]/[MDZ] metabolic ratio after exposure to MDZ for 1.5 h (at 48 h post-transfection), was dramatically increased by 1α-VD3 treatment. 1′-OH-MDZ formation was significantly lower in LS-180 cells treated with BERA/miR-27b-3p than control RNA (E). Values are mean ± SD of triplicate treatments. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001, compared to vehicle or control RNA group (Student׳s t-test).