Figure 2: XCorr-HR-SpO2 association with apnea, bradycardia, desaturation, and periodic breathing.
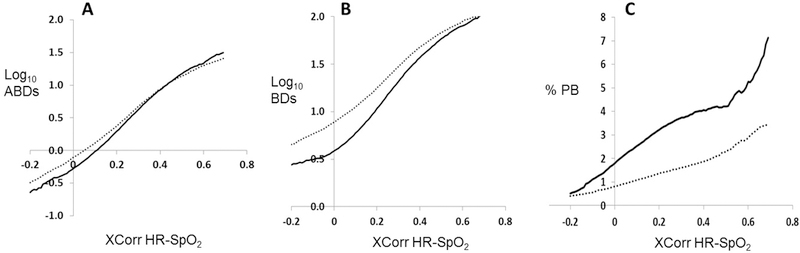
For 278 infants <1000 grams birthweight (dotted line) and 314 infants 1000–1499 grams (solid line), XCorr-HR-SpO2 is shown for all times infants were not on mechanical ventilation in relation to number of events of central apnea with associated bradycardia and desaturation (ABDs, panel A), BD events with or without central apnea (BDs, panel B), and percentage of time spent in periodic breathing (%PB, panel C). Note that, for panels A and B, the Y axis is plotted on a log base 10 scale. There was a very strong log-linear relationship between XCorr and ABD and BD (rho=.985 and .961 respectively) and a strong linear relationship with PB (rho=.933).
