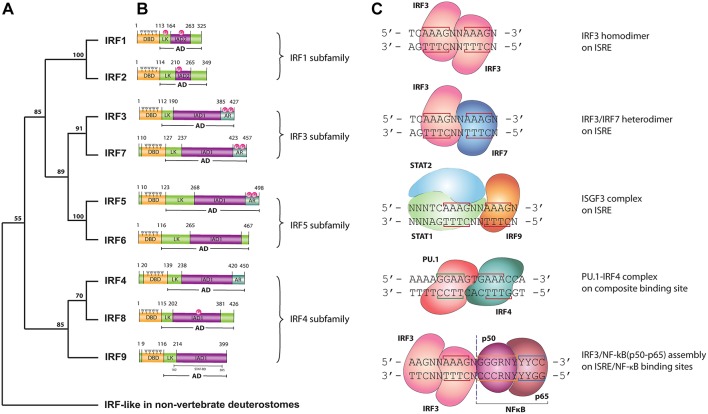
Figure 1.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the DNA-binding domain of IRF family proteins in vertebrates. Homologous protein sequences were searched using the NCBI BLAST server and aligned using ClustalW. Phylogenetic analyses were performed using the Neighbor-Joining method within the Mega 7.0 program. Data were analyzed using Poisson correction, and gaps were removed by pairwise deletion. The bootstrap values of the branches were obtained by testing the tree 10,000 times. Bootstrap values larger than 70% are shown next to the branches based on 10,000 replications. (B) Functional domains of human IRF proteins. DBD, DNA-binding domain; AD, activation domain; LK, linker region; IAD, IRF association domain type 1 (IAD1) or type 2 (IAD2); AR, auto-inhibitory region; P, phosphorylation site; 5W, five tryptophan repeats—“tryptophan cluster”; STAT-BD, STAT-binding domain. (C) DNA binding modes of IRFs. LINE—nucleotides involved in interaction with IRF—DBD; N, any nucleotide; R, purine; Y, pyrimidine. IRF3 homodimer, IRF3/IRF7 heterodimer and ISGF3 are bound to the consensus ISRE sequence with two ISRE half-sited “GAAA.” IRF4/PU.1 complex bind to the composite binding site, while NF-κB binds κB DNA element.