FIGURE 2: JFC1−/− neutrophils exhibit decreased polarization index upon fMLF stimulation and the defect is independent of impaired exocytosis.
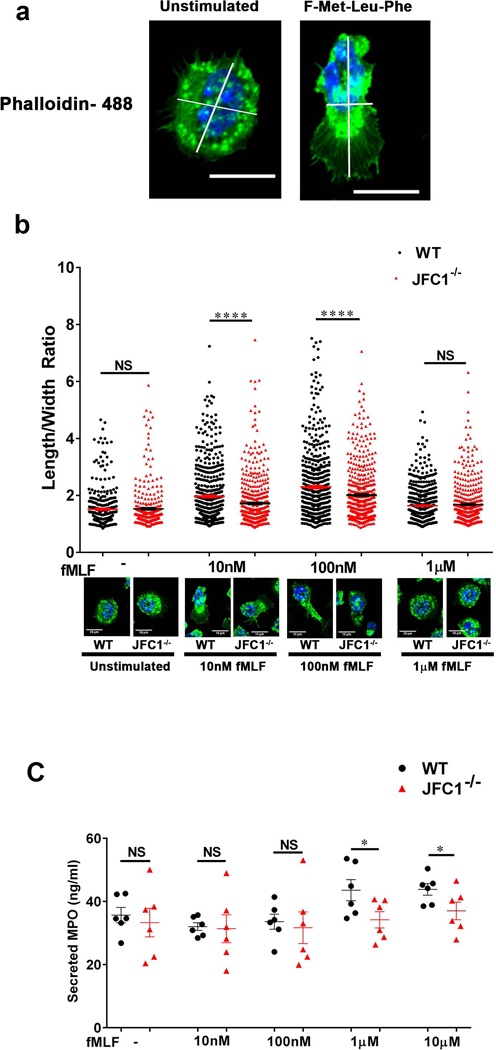
Mouse bone marrow neutrophils from WT and JFC1−/− mice were left unstimulated or stimulated with either 10nM, 100nM or 1μM fMLF for 10 min at 37° C, followed by fixation and staining with phalloidin-488. The length to width ratio of the cells were quantified using ImageJ software. (a) Representative images of unstimulated cells or cells stimulated with 100nM fMLF for 10 min. The scale bar represents 10μm. (Larger fields are shown in Supplementary Fig. S2a). (b) The elongation index of WT vs JFC1−/− cells calculated as the length to width ratio of the cell is indicated as mean ± SEM and was determined from 6 WT and 6 JFC1−/− mice. A minimum of 50 cells were measured from each mouse. A representative cell for WT and JFC1−/− neutrophils for each condition is shown. Larger fields can be seen in supplementary figure 2. **** p< 0.0001; NS, not significant. (c) Mouse bone marrow neutrophils from WT (shown in black) or JFC1−/− (shown in red) neutrophils were isolated and stimulated with the either 10nM, 100nM, 1μM or 10μM fMLF for 10 min at 37 °C, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in the cell supernatants was determined by ELISA. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, (n=6). Each symbol represents an individual mouse. *p<0.05; NS, not significant.
