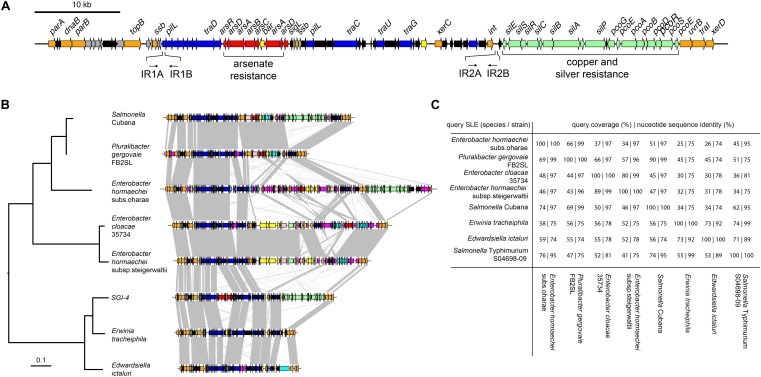
FIGURE 1.
Genetic map of Salmonella Genomic Island 4 (SGI-4) and phylogenetic relationship and gene synteny with SLEs. (A) Genetic diagram of Salmonella Genomic Island 4 (SGI-4); filled arrows indicate open reading frames with predicted functions based on sequence similarity for integration, excision and DNA processing (orange), type 4 secretion systems and conjugal transfer (blue), Cu and silver resistance (green), arsenic resistance (red), genes of unknown function commonly associated with ICE (gray), genes of unknown function not commonly associated with ICE (black). (B) Mid-point rooted maximum likelihood tree of eight SGI-4-like elements (SLEs) constructed using sequence variation in the core nucleotide sequence alignment of SLEs from diverse Enterobacteriaceae and genetic diagram of SLEs with regions of >75% nucleotide sequence identity (gray shading); filled arrows indicate open reading frames with the same designations as (A), with additional functions, cadmium, cobalt, zinc or mercury resistance (pink), transposase and insertion elements (purple), and a repressor protein lexA (brown). (C) Pair-wise sequence comparison of SLEs indicating the percentage of sequence exhibiting >60% identity and the mean nucleotide sequence identity of the shared sequence.