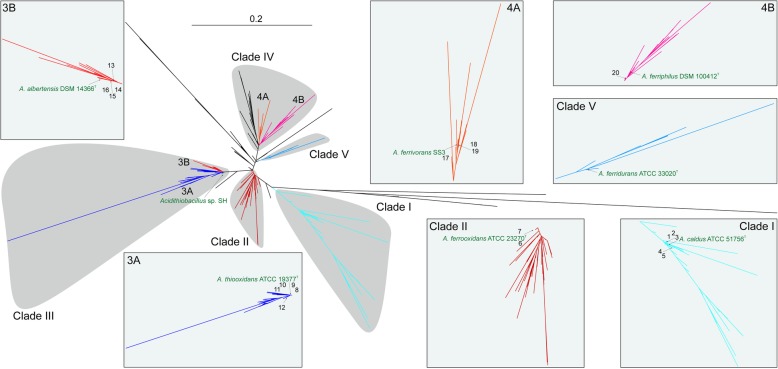
Fig. 1.
Maximum-likelihood (ML) phylogeny based on 16S rRNA gene sequences of Acidithiobacillus spp. Seven validated species are assigned into five clades, including A. caldus (Clade I), A. ferrooxidans (Clade II), A. thiooxidans (3A in Clade III), A. albertensis (3B in Clade III), A. ferrivorans (4A in Clade IV), A. ferriphilus (4B in Clade IV), and A. ferridurans (Clade V). These species are highlighted in different colors. Several strains of interest in various minor branches are also marked in this phylogenetic tree, including A. caldus strains DX (1), ZJ (2), ZBY (3), SM-1 (4), MTH-04 (5), A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 (6), Acidithiobacillus sp. GGI-221 (7), A. thiooxidans strains A01 (8), A02 (9), DMC (10), JYC-17 (11), BY-02 (12), ZBY (13), DXS-W (14), CLST (15), GD1-3 (16), A. ferrivorans strains YL15 (17), PRJEB5721 (18), CF27 (19), A. ferrooxidans BY0502 (20), and Acidithiobacillus sp. SH. Other branches representing unclear species are shown in black color. More details about these 602 16S rRNA gene sequences used in ML tree construction and their clade assignments are listed in Additional file 2: Table S2.