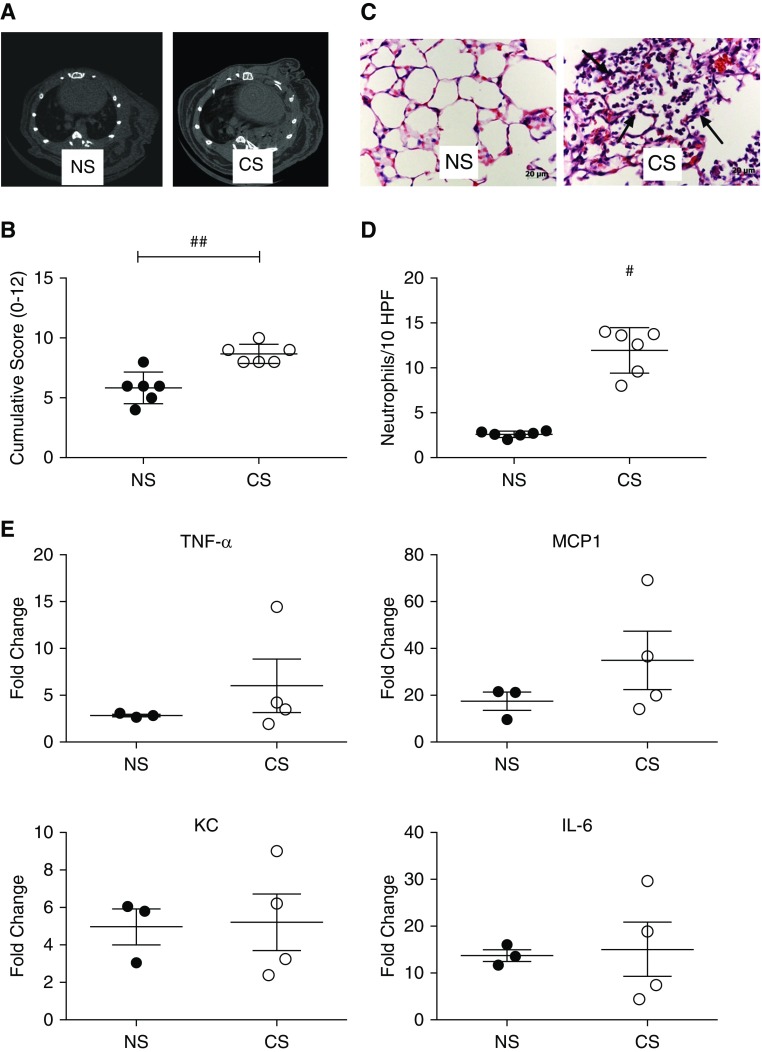
Figure 2.
Pretransplant recipient chronic CS exposure exacerbates lung transplant ischemia–reperfusion injury. Prolonged recipient CS exposure predisposes to (A) increased radiographically detectable lung injury and (B) histologically scored injury. ##P < 0.01. Representative histological images of lung injury show increased neutrophilic infiltrates, alveolar red blood cell accumulation, and fibrin deposition (C, arrows). Representative of n = 6. (D) Immunohistochemical quantification of neutrophils shows a significant increase in neutrophil numbers in CS versus NS as determined by image analysis of computerized randomly generated high-power fields (HPF). #P < 0.01. (E) Analysis of proinflammatory gene expression after transplant showed no significant differences in TNF-α, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), keratinocyte chemoattractant (KC), and IL-6.