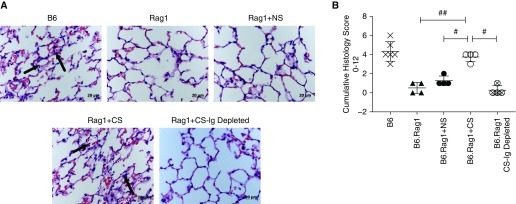
Figure 5.
Autoreactive antibodies generated by chronic smoke exposure reconstitute ischemia–reperfusion injury in antibody-deficient recipients. Histologic images of left lungs 6 hours after treatment are shown. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin–stained lung sections. B6 recipients demonstrate immune cell infiltrates, alveolar red blood cells, and neutrophil infiltrates (arrows). Serum reconstitution with either serum type–induced injury, but alveolar accumulation of neutrophils and red blood cells was significantly worse in CS-exposed mice (arrows) versus NS and recombination-activating protein 1 (Rag1) control mice. Reconstitution with antibody-depleted CS serum (Ig) resulted in an injury profile consistent with Rag1 control mice. (B) Histopathological quantification of injury demonstrates that adoptive transfer of CS serum induces significantly more injury. Scale bars: 20 μm. #P = 0.02 for CS versus NS; #P = 0.02 for CS versus Rag1 + CS-Ig-depleted serum control; ##P = 0.01 for CS versus Rag1 control mice.