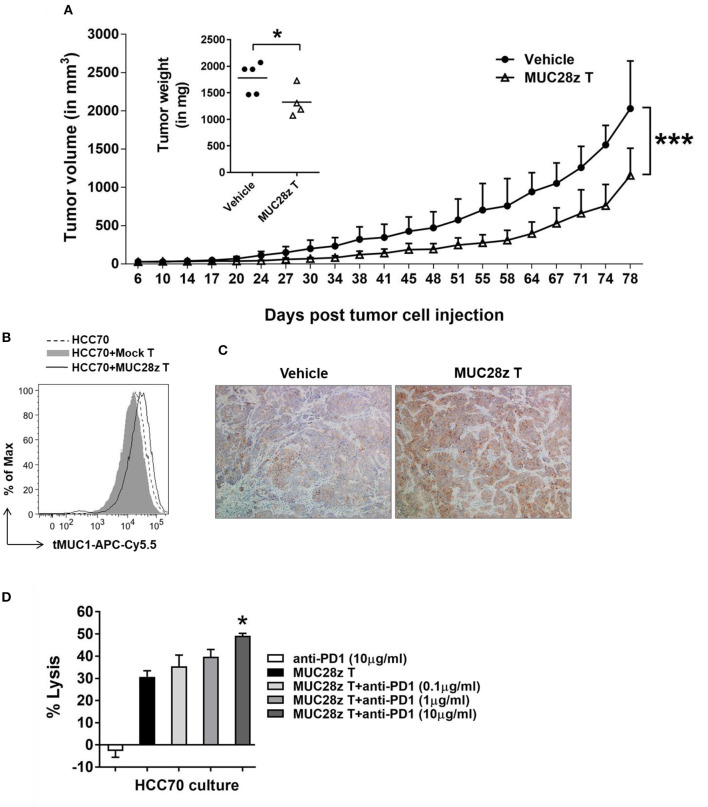
Figure 6.
MUC28z CAR T cells have long-term efficacy for HCC70 tumor reduction in vivo. (A) Decrease of HCC70 tumor burden by a single injection of MUC28z CAR T cells in vivo. HCC70 tumor were inoculated as described in Figure 5. When tumors were palpable, mice were randomized and received a single i.v. injection of PBS as vehicle control, or MUC28z CAR T cells on day 6 post-tumor cell challenge. Tumor growth was monitored by caliper measurement. Data are presented as mean ± SD. The statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA. ***p < 0.001. The insert shows the wet weight of resected tumor mass on day 81 at endpoint. *p < 0.05 (student t-test). (B) No tumor antigen loss while MUC28z CAR T cells were present in vitro. HCC70 cells were cultured alone or co-cultured with the mock T cells or MUC28z CAR T cells (E:T = 2:1) for 24 h. The viable HCC70 cells were analyzed for tMUC1 level. (C) Increased intensity of tMUC1 expression in MUC28z CAR T cells-treated HCC70 tumors. HCC70 tumor sections were prepared on day 81 at endpoint. Immunohistochemistry staining of tMUC1 was performed with TAB004 antibody. The brown staining shows tMUC1 positivity (100 × magnification). (D) Blocking PD1 enhanced the cytolytic response of MUC28z CAR T cells in vitro. HCC70 cells were co-cultured with MUC28z CAR T cells at E:T ratio of 2:1 for 24 h in the absence or presence of PD1 blocking antibody. The lysis of HCC70 cells was determined by MTT assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 when compared to the group of MUC28z CAR T cells alone (student t-test).