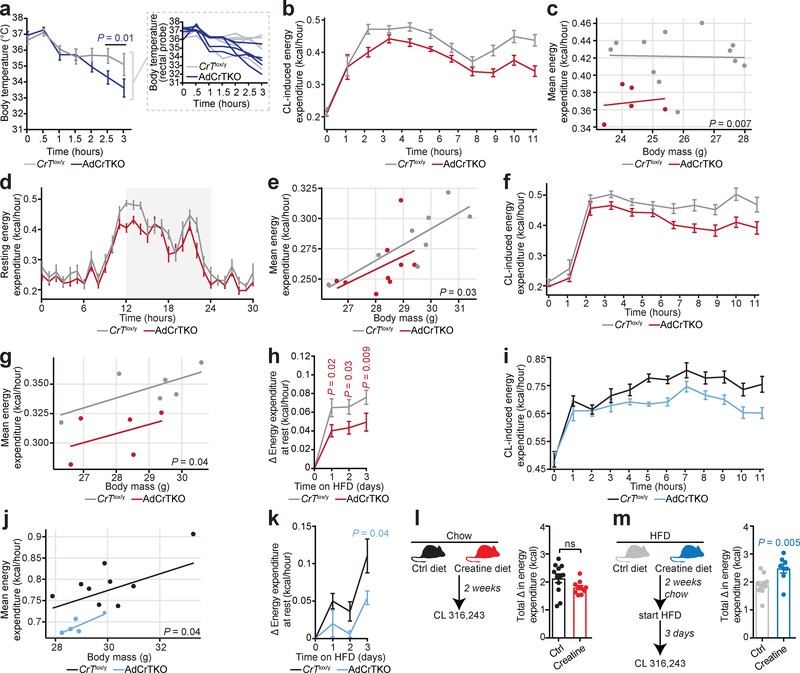
Fig. 2 |. AdCrTKO mice have impaired energy expenditure.
a, Body temperature of CrTlox/y and AdCrTKO mice (n = 5 mice per genotype, individual mouse temperatures are shown in inset). b, Energy expenditure at 30°C in response to CL 316,243 (CL) at 1 mg kg−1 (CrTlox/y, n = 12; AdCrTKO, n = 5). c, Regression plot of data from b (CrTlox/y, n = 12; AdCrTKO, n = 5). d, Resting energy expenditure in mice acutely (4 days) fed a high fat diet at 30°C (CrTlox/y, n = 8; AdCrTKO, n = 9). e, Regression plot of data from d (CrTlox/y, n = 8; AdCrTKO, n = 9). f, CL-dependent energy expenditure following acute high fat feeding at 30°C (CrTlox/y, n = 6; AdCrTKO, n = 5). g, Regression plot of data from f (CrTlox/y, n = 6; AdCrTKO, n = 5). h, Change in resting metabolic rate at 30°C in response to high fat feeding (CrTlox/y, n = 7; AdCrTKO, n = 9). i, CL-dependent energy expenditure following acute high fat feeding at 22°C (CrTlox/y, n = 9; AdCrTKO, n = 5). j, Regression plot of data from i (CrTlox/y, n = 9; AdCrTKO, n = 5). k, Change in resting metabolic rate at 22°C in response to high fat feeding (CrTlox/y, n = 11; AdCrTKO, n = 4). l, Experimental design for dietary chow creatine supplementation. Sustained energy expenditure (calculated as area under the curve) over 11 hours following i.p. administration of CL at 1 mg kg−1 (control chow diet, n = 12; creatine-supplemented chow diet, n = 10). m, Experimental design for dietary high fat creatine supplementation. Sustained energy expenditure (calculated as area under the curve) over 11 hours following i.p. administration of CL at 1 mg kg−1 (control high fat diet, n = 10; creatine-supplemented high fat diet, n = 8). Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. of biologically independent samples. Multiple two-tailed Student’s t-tests (a, h, k-m); ANCOVA (c, e, g, j).