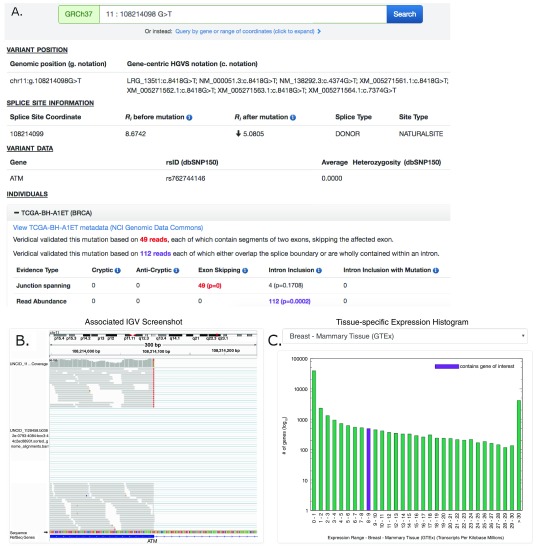
Figure 1. Screenshot of ATM:g.108214098G>T Results Provided By ValidSpliceMut Website.
( A) The ‘Variant Position’ heading displays the variant of interest in g. notation, and provides a link which queries the Mutalyzer API to obtain the variant coordinate in a gene-centric c. mutation format. Variant-specific and splice site-specific tabular results are presented under the headings “Splice Site Information” and “Variant Data”. Results are organized by TCGA and ICGC sample IDs harboring the mutation within a series of expandable panels. A link is provided to patient tumor metadata on the GDC data portal. Each panel consists of read counts and p-values by Veridical evidence type. Significant p-values (≤ 0.05) are highlighted in bold. Evidence types deemed “strongly corroborating” (Viner et al. 2014) are color coded and correspond to the dynamically generated text appearing above the table. ( B) An integrative genome viewer (IGV) image showing alignment of expressed sequence reads. IGV screenshots are provided only for mutations present <1% of population (in dbSNP 150), with ≥ 5 junction-spanning reads, and are highly significant (p < 0.01) for cryptic splicing, exon skipping, and/or intron inclusion with mutation. A specific IGV screenshot for this sample captures the region surrounding the mutation. Here, several RNA-Seq reads show skipping of the affected exon. ( C) A dynamically generated histogram presents expression levels of all genes for a selected normal tissue type. Genes are grouped into bins based on expression level, denoted on the x-axis. The number of genes present in each bin is shown on the y-axis (log 10 scale). The histogram key indicates the expression range of the variant-containing gene. Tissue type can be changed via a drop-down list.