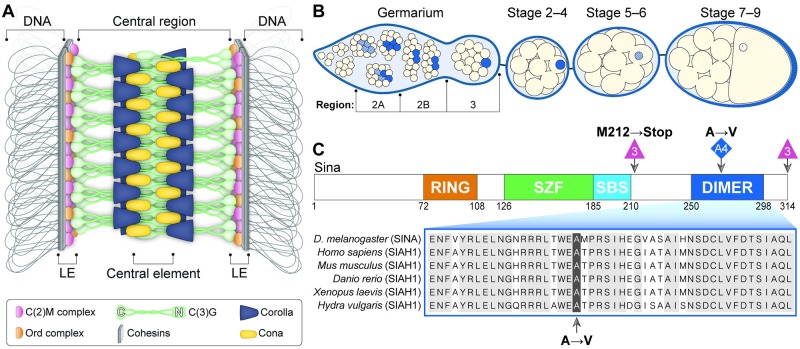
Fig 1. SC assembly in the Drosophila ovary.
(A) Current model of the Drosophila SC along the euchromatin. (B) Schematic of the timing of SC assembly and disassembly in Drosophila females. At the initiation of meiosis (region 2A), SC components (blue) load along the chromosomes in up to four nuclei of the cyst. As the cyst progresses through the germarium (region 2B–3), the SC is progressively disassembled from all nuclei but the pro-oocyte. SC progressively disassembles from the chromosome arms in the oocyte at approximately stage 5–7 but persists at the centromeres for additional stages. (C) The sinaA4 mutation affects a conserved amino acid in the dimerization domain of the Sina protein. The domains of the Sina protein are as described in [16]. The RING (Really Interesting New Gene) domain has E3 ligase catalytic activity, the SZF (SIAH-type zinc finger) domain includes a dual zinc-finger motif, the SBS (substrate-binding site) recognizes some targets, and the DIMER (dimerization) domain allows for formation of homo- and heterodimers of Sina family proteins. The location of the sinaA4 mutation (highlighted) in the DIMER domain is shown in comparison to sequences from Siah1 homologs in other species (for full homology see [16]). The location of the deletion breakpoints and the resulting early stop of the sina3 mutation is also shown.